Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor
- PMID: 19551844
- PMCID: PMC6357774
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23054
Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor
Abstract
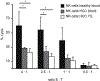
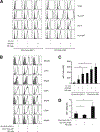
Several immune suppressive mechanisms that evade the host immune response have been described in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); one of these mechanisms is expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). MDSCs have been shown to inhibit T cell responses in tumor-bearing mice, but little is known about these cells in humans. Here, we have analyzed and characterized the effect of MDSCs on the innate immune system, in particular, their interaction with natural killer (NK) cells in patients with HCC. MDSCs from patients with HCC inhibited autologous NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion when cultured together in vitro. This suppression was dependent on cell contact, but did not rely on the arginase activity of MDSCs, which is a hallmark function of these cells. However, MDSC-mediated inhibition of NK cell function was dependent mainly on the NKp30 on NK cells.
Conclusion: Our study suggests a new role for MDSCs in patients with HCC in disarming the innate immune system and further contributing to the immune suppressor network in these patients. These findings have important implications when designing immunotherapy protocols.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report
Figures
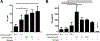
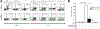


References
-
- Serafini P, Borrello I, Bronte V. Myeloid suppressor cells in cancer: recruitment, phenotype, properties, and mechanisms of immune suppression. Semin Cancer Biol 2006;16:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Pak AS, Wright MA, Matthews JP, Collins SL, Petruzzelli GJ, Young MR. Mechanisms of immune suppression in patients with head and neck cancer: presence of CD34(+) cells which suppress immune functions within cancers that secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res 1995;1:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Zea AH, Rodriguez PC, Atkins MB, Hernandez C, Signoretti S, Zabaleta J,et al.Arginase-producingmyeloidsuppressorcellsinrenalcellcarcinoma patients: a mechanism of tumor evasion. Cancer Res 2005;65:3044–3048. - PubMed
-
- Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, et al. Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol 2001;166:678–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
