Electrocardiogram changes and arrhythmias in venlafaxine overdose
- PMID: 19552753
- PMCID: PMC2686075
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03382.x
Electrocardiogram changes and arrhythmias in venlafaxine overdose
Abstract
Aims: To investigate serial electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters, haemodynamic changes and arrhythmias following venlafaxine overdose.
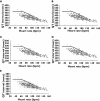
Methods: The study included 369 venlafaxine overdoses in 273 patients presenting to a toxicology unit where an ECG was available. Demographic information, details of ingestion, haemodynamic effects [heart rate and blood pressure (BP)] and complications (arrhythmias and conduction defects) were obtained. ECG parameters (QT, QRS) were measured manually and analysed by visual inspection, including plotting QT-HR pairs on a QT nomogram.
Results: The median ingested dose was 1500 mg [interquartile range (IQR) 600-3000 mg; range 75-13 500 mg). Tachycardia occurred in 54% and mild hypertension (systolic BP >140 mmHg) in 40%. Severe hypertension (systolic BP >180 mmHg) and hypotension (systolic BP <90 mmHg) occurred in 3% and 5%, respectively. No arrhythmias occurred based on continuous telemetry, and conduction defects were found in only seven of 369 admissions; five of these conduction defects were pre-existing abnormalities. In 22 admissions [6%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 4-10] there was an abnormal QT-HR pair, with larger doses being more likely to be associated with an abnormal QT. The median maximum QRS width was 85 ms (IQR 80-90 ms; range 70-145 ms) and the QRS was greater than 120 ms in only 24 admissions (7%, 95% CI 4-10).
Conclusions: Venlafaxine overdose causes only minor abnormalities in the QT and QRS intervals, unlikely to be associated with major arrhythmias, except possibly with large doses.
Figures
References
-
- Whyte IM, Dawson AH, Buckley NA. Relative toxicity of venlafaxine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in overdose compared to tricyclic antidepressants. QJM. 2003;96:369–74. - PubMed
-
- Hojer J, Hulting J, Salmonson H. Fatal cardiotoxicity induced by venlafaxine overdosage. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2008;46:336–7. - PubMed
-
- Peano C, Leikin JB, Hanashiro PK. Seizures, ventricular tachycardia, and rhabdomyolysis as a result of ingestion of venlafaxine and lamotrigine. Ann Emerg Med. 1997;30:704–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

