The role of NF-kappaB factor REL2 in the Aedes aegypti immune response
- PMID: 19552893
- PMCID: PMC2702699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.01.007
The role of NF-kappaB factor REL2 in the Aedes aegypti immune response
Abstract
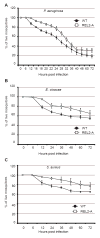
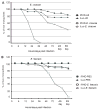
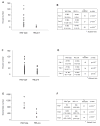
Mosquitoes transmit numerous diseases that continue to be an enormous burden on public health worldwide. Transgenic mosquitoes impervious to vector-borne pathogens, in concert with vector control and drug and vaccine development, comprise an arsenal of means anticipated to defeat mosquito-spread diseases in the future. Mosquito transgenesis allows tissue-specific manipulation of their major immune pathways and enhances the ability to study mosquito-pathogen interactions. Here, we report the generation of two independent transgenic strains of Aedes aegypti overexpressing the NF-?B transcriptional factor REL2, a homologue of Drosophila Relish, which is shown to be under the control of the vitellogenin promoter in the mosquito fat body after a blood meal. We show that this REL2 overexpression in the fat body results in transcriptional activation of Defensins A, C, and D, and Cecropins A and N, as well as translation and secretion of Defensin A protein into the hemolymph. We also demonstrate that induction of REL2 results in the increased resistance of the mosquito to tested Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Importantly, induction of transgenic REL2 leads to the significant decrease in susceptibility of A. aegypti to Plasmodium gallinaceum infection. Consistently, RNAi knockdown of REL2 in wild-type mosquitoes results in a delay in Defensin A and Cecropin A expression in response to infection and in increased susceptibility to both bacteria and P. gallinaceum. Moreover, our transgenic assays demonstrate that the N-terminus of the mosquito REL2, which includes the His/Gln-rich and serine-rich regions, plays a role in its transactivation properties.
Figures





References
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: Ten Years After. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Christophides GK, Zdobnov E, Barillas-Mury C, Birney E, Blandin S, Blass C, Brey PT, Collins FH, Danielli A, Dimopoulos G, Hetru C, Hoa NT, Hoffmann JA, Kanzok SM, Letunic I, Levashina EA, Loukeris TG, Lycett G, Meister S, Michel K, Moita LF, Müller HM, Osta MA, Paskewitz SM, Reichhart JM, Rzhetsky A, Troxler L, Vernick KD, Vlachou D, Volz J, von Mering C, Xu J, Zheng L, Bork P, Kafatos FC. Immunity-related genes and gene families in Anopheles gambiae. Science. 2002;298:59–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

