BRCA2-dependent homologous recombination is required for repair of Arsenite-induced replication lesions in mammalian cells
- PMID: 19553191
- PMCID: PMC2731915
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp538
BRCA2-dependent homologous recombination is required for repair of Arsenite-induced replication lesions in mammalian cells
Abstract
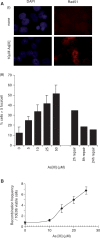
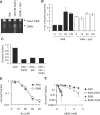
Arsenic exposure constitutes one of the most widespread environmental carcinogens, and is associated with increased risk of many different types of cancers. Here we report that arsenite (As[III]) can induce both replication-dependent DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) and homologous recombination (HR) at doses as low as 5 microM (0.65 mg/l), which are within the typical doses often found in drinking water in contaminated areas. We show that the production of DSBs is dependent on active replication and is likely to be the result of conversion of a DNA single-strand break (SSB) into a toxic DSB when encountered by a replication fork. We demonstrate that HR is required for the repair of these breaks and show that a functional HR pathway protects against As[III]-induced cytotoxicity. In addition, BRCA2-deficient cells are sensitive to As[III] and we suggest that As[III] could be exploited as a therapy for HR-deficient tumours such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutated breast and ovarian cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Chiou HY, et al. Incidence of internal cancers and ingested inorganic arsenic: a seven-year follow-up study in Taiwan. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1296–1300. - PubMed
-
- Liu YT, Chen Z. A retrospective lung cancer mortality study of people exposed to insoluble arsenic and radon. Lung Cancer. 1996;14(Suppl. 1):S137–S148. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Wang CJ. Ecological correlation between arsenic level in well water and age-adjusted mortality from malignant neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1990;50:5470–5474. - PubMed
-
- Tsai SM, Wang TN, Ko YC. Mortality for certain diseases in areas with high levels of arsenic in drinking water. Arch. Environ. Health. 1999;54:186–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

