Degradation of nanoRNA is performed by multiple redundant RNases in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 19553197
- PMCID: PMC2731908
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp527
Degradation of nanoRNA is performed by multiple redundant RNases in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
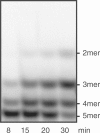
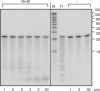
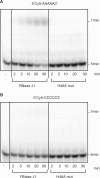
Escherichia coli possesses only one essential oligoribonuclease (Orn), an enzyme that can degrade oligoribonucleotides of five residues and shorter in length (nanoRNA). Firmicutes including Bacillus subtilis do not have an Orn homolog. We had previously identified YtqI (NrnA) as functional analog of Orn in B. subtilis. Screening a genomic library from B. subtilis for genes that can complement a conditional orn mutant, we identify here YngD (NrnB) as a second nanoRNase in B. subtilis. Like NrnA, NrnB is a member of the DHH/DHHA1 protein family of phosphoesterases. NrnB degrades nanoRNA 5-mers in vitro similarily to Orn. Low expression levels of NrnB are sufficient for orn complementation. YhaM, a known RNase present in B. subtilis, degrades nanoRNA efficiently in vitro but requires high levels of expression for only partial complementation of the orn(-) strain. A triple mutant (nrnA(-), nrnB(-), yhaM(-)) in B. subtilis is viable and shows almost no impairment in growth. Lastly, RNase J1 seems also to have some 5'-to-3' exoribonuclease activity on nanoRNA and thus can potentially finish degradation of RNA. We conclude that, unlike in E. coli, degradation of nanoRNA is performed in a redundant fashion in B. subtilis.
Figures




References
-
- Condon C. Maturation and degradation of RNA in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Cheng ZF, Deutscher MP. Purification and characterization of the Escherichia coli exoribonuclease RNase R. Comparison with RNase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:21624–21629. - PubMed
-
- Amblar M, Barbas A, Fialho AM, Arraiano CM. Characterization of the functional domains of Escherichia coli RNase II. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;360:921–933. - PubMed
-
- Vincent HA, Deutscher MP. Substrate recognition and catalysis by the exoribonuclease RNase R. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:29769–29775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

