Preclinical characterization of 1-7F9, a novel human anti-KIR receptor therapeutic antibody that augments natural killer-mediated killing of tumor cells
- PMID: 19553639
- PMCID: PMC2756126
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206532
Preclinical characterization of 1-7F9, a novel human anti-KIR receptor therapeutic antibody that augments natural killer-mediated killing of tumor cells
Abstract
Inhibitory-cell killer immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) negatively regulate natural killer (NK) cell-mediated killing of HLA class I-expressing tumors. Lack of KIR-HLA class I interactions has been associated with potent NK-mediated antitumor efficacy and increased survival in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients upon haploidentical stem cell transplantation from KIR-mismatched donors. To exploit this pathway pharmacologically, we generated a fully human monoclonal antibody, 1-7F9, which cross-reacts with KIR2DL1, -2, and -3 receptors, and prevents their inhibitory signaling. The 1-7F9 monoclonal antibody augmented NK cell-mediated lysis of HLA-C-expressing tumor cells, including autologous AML blasts, but did not induce killing of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells, suggesting a therapeutic window for preferential enhancement of NK-cell cytotoxicity against malignant target cells. Administration of 1-7F9 to KIR2DL3-transgenic mice resulted in dose-dependent rejection of HLA-Cw3-positive target cells. In an immunodeficient mouse model in which inoculation of human NK cells alone was unable to protect against lethal, autologous AML, preadministration of 1-7F9 resulted in long-term survival. These data show that 1-7F9 confers specific, stable blockade of KIR, boosting NK-mediated killing of HLA-matched AML blasts in vitro and in vivo, providing a preclinical basis for initiating phase 1 clinical trials with this candidate therapeutic antibody.
Figures

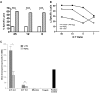
 , ■, ▲, and ● represent cell lines expressing KIR2DL1, KIR2DS1, KIR2DL3, and KIR2DS2, respectively. Mean and SD of data collected in 2 independent experiments are shown.
, ■, ▲, and ● represent cell lines expressing KIR2DL1, KIR2DS1, KIR2DL3, and KIR2DS2, respectively. Mean and SD of data collected in 2 independent experiments are shown.
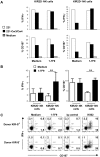

 ). (The NK cells were isolated from a healthy donor having the same HLA class I allotype groups as the AML target cells.) E:T ratio was 15:1. Results were analyzed by Student t test (***P < .005). (C) NOD-SCID mice infused with autologous NK cells and AML target cells at 1:3 E:T ratio died of leukemia within 65 days. Treatment with 1-7F9 (250 μg/mouse) rescued mice challenged with NK and AML cells at an E:T ratio of 1:12, but not at an E:T of 1:18. N = 5 mice per group. Results have been analyzed by Kaplan Meier log rank test (***P < .005). Similar results were obtained in a repeat experiment.
). (The NK cells were isolated from a healthy donor having the same HLA class I allotype groups as the AML target cells.) E:T ratio was 15:1. Results were analyzed by Student t test (***P < .005). (C) NOD-SCID mice infused with autologous NK cells and AML target cells at 1:3 E:T ratio died of leukemia within 65 days. Treatment with 1-7F9 (250 μg/mouse) rescued mice challenged with NK and AML cells at an E:T ratio of 1:12, but not at an E:T of 1:18. N = 5 mice per group. Results have been analyzed by Kaplan Meier log rank test (***P < .005). Similar results were obtained in a repeat experiment.Comment in
-
NK antibody therapy: KIR-ative intent.Blood. 2009 Sep 24;114(13):2567-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-230904. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19779042 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:503–510. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Bottino C, Castriconi R, Moretta L, Moretta A. Cellular ligands of activating NK receptors. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:221–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

