Hematocrit and mean arterial blood pressure in pre- and postmenopause women
- PMID: 19554088
- PMCID: PMC2697582
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s5798
Hematocrit and mean arterial blood pressure in pre- and postmenopause women
Abstract
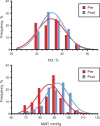
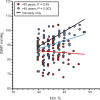
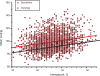
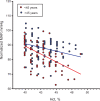
The relationship between mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and hematocrit (Hct) was studied in pre- and postmenopause women in the city of Durango, Mexico. Premenopause women show a negative trend between parameters that is not statistically significant. MAP and Hct are directly related in postmenopause women (p < 0.01). It is proposed that that this MAP/Hct relationship is in part due to differences in endothelial function where menopause decreases the capacity of the endothelium to respond to increased blood viscosity and shears stress, leading to the increased production of vasodilator mediators to compensate for changes in blood viscosity due to changes in Hct. Comparison with a large group of postmenopause women in the city of Stockholm showed identical trends.
Keywords: blood pressure; blood viscosity; endothelial dysfunction; hematocrit; menopause.
Figures
References
-
- Assmann G, et al. Coronary heart disease: reducing the risk: a worldwide view. International Task Force for the Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation. 1999;100:1930–1938. - PubMed
-
- Maturana MA. Menopause, estrogens, and endothelial dysfunction: current concepts. Clinics. 2007;62:77–86. - PubMed
-
- Clapauch R, et al. Use of vascular Doppler ultrasound to detect acute estradiol vascular effect in postmenopausal women. Clinics. 2007;62:673–678. - PubMed
-
- Mercuro G. Impaired forearm blood flow and vasodilator reserve in healthy postmenopausal women. Am Heart J. 1999;137:692–697. - PubMed
-
- de Simone G. Relation of blood viscosity to demographic and physiologic variables and to cardiovascular risk factors in apparently normal adults. Circulation. 1990;81:107–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

