Kank proteins: structure, functions and diseases
- PMID: 19554261
- PMCID: PMC11115667
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0038-y
Kank proteins: structure, functions and diseases
Abstract
The Kank family of proteins, Kank1-Kank4, are characterized by their unique structure, coiled-coil motifs in the N-terminal region, and ankyrin-repeats in the C-terminal region, with an additional motif, the KN motif, at the N-terminus. Kank1 was obtained by positional cloning of a tumor suppressor gene in renal cell carcinoma, while the other members were found by homology search. The family is involved in the regulation of actin polymerization and cell motility through signaling pathways containing PI3K/Akt and/or unidentified modulators/effectors. Their relationship to diseases such as cancer, and to neuronal and developmental disorders, will be an important subject of future study.
Figures
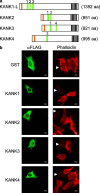

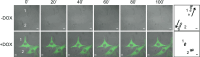

References
-
- Zhu Y, Kakinuma N, Wang Y, Kiyama R. Kank proteins: a new family of ankyrin-repeat domain-containing proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1780:128–133. - PubMed
-
- Rodley P, Hatano N, Nishikawa NS, Roy BC, Sarkar S, Kiyama R. A differential genomic cloning method for cancer study: an outline and applications. Recent Res Dev Mol Biol. 2003;1:13–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

