Alcohol inhibition of neurogenesis: a mechanism of hippocampal neurodegeneration in an adolescent alcohol abuse model
- PMID: 19554644
- PMCID: PMC2861155
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.20665
Alcohol inhibition of neurogenesis: a mechanism of hippocampal neurodegeneration in an adolescent alcohol abuse model
Abstract
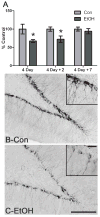
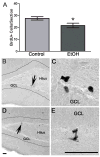
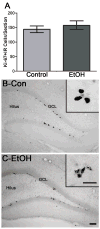
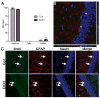
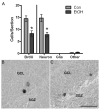
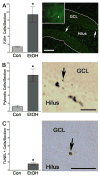
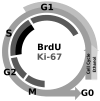
Adolescents diagnosed with an alcohol use disorder show neurodegeneration in the hippocampus, a region important for learning, memory, and mood regulation. This study examines a potential mechanism by which excessive alcohol intake, characteristic of an alcohol use disorder, produces neurodegeneration. As hippocampal neural stem cells underlie ongoing neurogenesis, a phenomenon that contributes to hippocampal structure and function, we investigated aspects of cell death and cell birth in an adolescent rat model of an alcohol use disorder. Immunohistochemistry of various markers along with Bromo-deoxy-Uridine (BrdU) injections were used to examine different aspects of neurogenesis. After 4 days of binge alcohol exposure, neurogenesis was decreased by 33 and 28% at 0 and 2 days after the last dose according to doublecortin expression. To determine whether this decrease in neurogenesis was due to effects on neural stem cell proliferation, quantification of BrdU-labeled cells revealed a 21% decrease in the dentate gyrus of alcohol-exposed brains. Cell survival and phenotype of BrdU-labeled cells were assessed 28 days after alcohol exposure and revealed a significant, 50% decrease in the number of surviving cells in the alcohol-exposed group. Reduced survival was supported by significant increases in the number of pyknotic-, FluoroJade B positive-, and TUNEL-positive cells. However, so few cells were TUNEL-positive that cell death is likely necrotic in this model. Although alcohol decreased the number of newborn cells, it did not affect the percentage of cells that matured into neurons (differentiation). Thus, our data support that in a model of an adolescent alcohol use disorder, neurogenesis is impaired by two mechanisms: alcohol-inhibition of neural stem cell proliferation and alcohol effects on new cell survival. Remarkably, alcohol inhibition of neurogenesis may outweigh the few dying cells per section, which implies that alcohol inhibition of neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal neurodegeneration in alcohol use disorders.
2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124(3):319–35. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A. Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(11):1458–63. - PubMed
-
- Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG. Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 2003;467(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Cameron HA, McKay RD. Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol. 2001;435(4):406–17. - PubMed
-
- Canales JJ. Adult neurogenesis and the memories of drug addiction. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

