Acute pancreatitis at the beginning of the 21st century: the state of the art
- PMID: 19554647
- PMCID: PMC2702102
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.2945
Acute pancreatitis at the beginning of the 21st century: the state of the art
Abstract
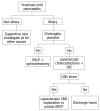
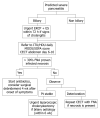
Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammatory disease of the pancreas which can lead to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome with significant morbidity and mortality in 20% of patients. Gallstones and alcohol consumption are the most frequent causes of pancreatitis in adults. The treatment of mild acute pancreatitis is conservative and supportive; however severe episodes characterized by necrosis of the pancreatic tissue may require surgical intervention. Advanced understanding of the pathology, and increased interest in assessment of disease severity are the cornerstones of future management strategies of this complex and heterogeneous disease in the 21st century.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute pancreatitis: A narrative review.J Pak Med Assoc. 2024 May;74(5):953-958. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.9280. J Pak Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38783446 Review.
-
Acute pancreatitis.Lancet. 2008 Jan 12;371(9607):143-52. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60107-5. Lancet. 2008. PMID: 18191686 Review.
-
Assessment of the course of acute pancreatitis in the light of aetiology: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 21;10(1):17936. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74943-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33087766 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pancreatitis and organ failure: pathophysiology, natural history, and management strategies.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004 Apr;6(2):99-103. doi: 10.1007/s11894-004-0035-0. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15191686 Review.
-
Biliary pancreatitis: a review. Emphasizing appropriate endoscopic intervention.J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999 Mar;28(2):97-109. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199903000-00004. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10078816 Review.
Cited by
-
Change of Both Endocrine and Exocrine Insufficiencies After Acute Pancreatitis in Non-Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Population-Based Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Jul;94(27):e1123. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001123. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26166112 Free PMC article.
-
Factors predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis in elderly patients.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jan;33(1):183-192. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01523-1. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 32185694
-
Laparoscopic necrosectomy for acute necrotising pancreatitis: Retrospective analysis of a decade-long experience from a tertiary centre.J Minim Access Surg. 2024 Apr 1;20(2):127-135. doi: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_215_22. Epub 2024 Mar 28. J Minim Access Surg. 2024. PMID: 38557646 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pancreatitis. A more common and severe complication of gallstones in males.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2015 Apr;9(2):141-5. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2015. PMID: 26309432 Free PMC article.
-
An update on pancreatic pathophysiology (do we have to rewrite pancreatic pathophysiology?).Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014 Feb;164(3-4):57-62. doi: 10.1007/s10354-013-0260-y. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 24468827 Review.
References
-
- Sbarounis CN. Did Alexander the Great die of acute pancreatitis? J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;24:294–296. - PubMed
-
- Bernard C. Lecons de physiologie experimentale appliquee a la medecine. 2 vols. Paris: Bailliere, 1855-1856.
-
- Fitz RH. Acute Pancreatitis: a consideration of pancreatic hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, suppurative and gangrenous pancreatitis of disseminated fat necrosis. Boston Med Surg J. 1889;120:181–235.
-
- Chiari H. Über selbstverdauung des menschlichen Pancreas. Z Heilk. 1896;17:69–96.
-
- Opie EL. The etiology of acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Johns Hopks Hosp Bull. 1901;12:182–188.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

