The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells
- PMID: 19555289
- PMCID: PMC3086722
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135600
The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells
Abstract
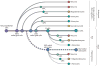
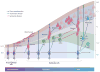
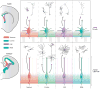
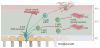
Glial cells were long considered end products of neural differentiation, specialized supportive cells with an origin very different from that of neurons. New studies have shown that some glial cells--radial glia (RG) in development and specific subpopulations of astrocytes in adult mammals--function as primary progenitors or neural stem cells (NSCs). This is a fundamental departure from classical views separating neuronal and glial lineages early in development. Direct visualization of the behavior of NSCs and lineage-tracing studies reveal how neuronal lineages emerge. In development and in the adult brain, many neurons and glial cells are not the direct progeny of NSCs, but instead originate from transit amplifying, or intermediate, progenitor cells (IPCs). Within NSCs and IPCs, genetic programs unfold for generating the extraordinary diversity of cell types in the central nervous system. The timing in development and location of NSCs, a property tightly linked to their neuroepithelial origin, appear to be the key determinants of the types of neurons generated. Identification of NSCs and IPCs is critical to understand brain development and adult neurogenesis and to develop new strategies for brain repair.
Figures

References
-
- Aaku-Saraste E, Oback B, Hellwig A, Huttner WB. Neuroepithelial cells downregulate their plasma membrane polarity prior to neural tube closure and neurogenesis. Mech Dev. 1997;69:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre A, Dupree JL, Mangin JM, Gallo V. A functional role for EGFR signaling in myelination and remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:990–1002. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Horizontal compartmentation in the germinal matrices and intermediate zone of the embryonic rat cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol. 1990a;107:36–47. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol. 1990b;301:325–42. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

