In vitro cytotoxicity of novel pro-apoptotic agent DM-PIT-1 in PEG-PE-based micelles alone and in combination with TRAIL
- PMID: 19555308
- PMCID: PMC3071122
- DOI: 10.1080/10717540802517951
In vitro cytotoxicity of novel pro-apoptotic agent DM-PIT-1 in PEG-PE-based micelles alone and in combination with TRAIL
Abstract
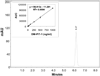
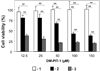
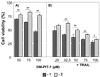
The purpose of this study was to develope and characterize a micellar formulations of N-{[(2-hydroxy-5- nitrophenyl)amino]carbonothioyl}-3,5-dimethylbenzamide (DM-PIT-1)-a new small molecule non-lipid antagonist of phopshotidylinositol-3.4.5-triphopshate and inhibitor of the PI3-kinase pathway. Micelle-forming PEG(2000)-PE was used to solubilize DM-PIT-1. To improve the specificity of the micellar DM-PIT-1, cancer-targeting anti-nucleosomal mAb2C5 antibodies as well as Tumor necrosis factor- Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) were attached to the surface of polymeric micelles. DM-PIT-1 was effectively incorporated (> 70%) into 14-16 nm micelles, which had a negative surface zeta potential of 4-5 mV. Micellar DM-PIT-1 demonstrated high in vitro cytotoxicity against various cancer cells. An improved potency of the dual-activity DM-PIT-1/TRAIL combination nanoparticles in inducing death of TRAIL-resistant cancer cells was shown. Efficacy of the TRAIL therapy was enhanced by combining it with the 2C5 antibody cancer-targeted micellar form of DM-PIT-1. In conclusion, DM-PIT-1 micellar preparations can be used for targeted combination therapy against TRAIL-resistant cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Ballestrero A, Montemurro F, Gonella R, Capaldi A, Danova M, Friedman D, Puglisi M, Aglietta M, Patrone F. Dose-dense vinorelbine and paclitaxel with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in metastatic breast cancer patients: anti-tumor activity and peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization capability. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;82(3):185–190. - PubMed
-
- Chawla-Sarkar M, Bae SI, Reu FJ, Jacobs BS, Lindner DJ, Borden EC. Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs (XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11(8):915–923. - PubMed
-
- Elbayoumi TA, Pabba S, Roby A, Torchilin VP. Antinucleosome antibody-modified liposomes and lipid-core micelles for tumor-targeted delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents. J Liposome Res. 2007;17(1):1–14. - PubMed
-
- Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A. Cremophor EL: the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(13):1590–1598. - PubMed
-
- Guo F, Nimmanapalli R, Paranawithana S, Wittman S, Griffin D, Bali P, O'Bryan E, Fumero C, Wang HG, Bhalla K. Ectopic overexpression of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac/DIABLO) or cotreatment with N-terminus of Smac/DIABLO peptide potentiates epothilone B derivative-(BMS 247550) and Apo-2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Blood. 2002;99(9):3419–3426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
