Updated evidence-based treatment algorithm in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 19555861
- PMCID: PMC3686287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.017
Updated evidence-based treatment algorithm in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
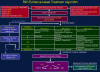
Uncontrolled and controlled clinical trials with different compounds and procedures are reviewed to define the risk-benefit profiles for therapeutic options in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). A grading system for the level of evidence of treatments based on the controlled clinical trials performed with each compound is used to propose an evidence-based treatment algorithm. The algorithm includes drugs approved by regulatory agencies for the treatment of PAH and/or drugs available for other indications. The different treatments have been evaluated mainly in idiopathic PAH, heritable PAH, and in PAH associated with the scleroderma spectrum of diseases or with anorexigen use. Extrapolation of these recommendations to other PAH subgroups should be done with caution. Oral anticoagulation is proposed for most patients; diuretic treatment and supplemental oxygen are indicated in cases of fluid retention and hypoxemia, respectively. High doses of calcium-channel blockers are indicated only in the minority of patients who respond to acute vasoreactivity testing. Nonresponders to acute vasoreactivity testing or responders who remain in World Health Organization (WHO) functional class III, should be considered candidates for treatment with either an oral phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor or an oral endothelin-receptor antagonist. Continuous intravenous administration of epoprostenol remains the treatment of choice in WHO functional class IV patients. Combination therapy is recommended for patients treated with PAH monotherapy who remain in WHO functional class III. Atrial septostomy and lung transplantation are indicated for refractory patients or where medical treatment is unavailable.
Figures
References
-
- Rich S, Kaufmann E, Levy PS. The effect of high doses of calcium-channel blockers on survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:76–81. - PubMed
-
- Rich S, Brundage BH. High-dose calcium channel-blocking therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: evidence for long-term reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure and regression of right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 1987;76:135–41. - PubMed
-
- Raffy O, Azarian R, Brenot F, et al. Clinical significance of the pulmonary vasodilator response during short-term infusion of prostacyclin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1996;93:484–8. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Maislin G, Fishman AP. Vasodilator therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension in children. Circulation. 1999;99:1197–208. - PubMed
-
- Sitbon O, Humbert M, Jaïs X, et al. Long-term response to calcium channel blockers in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2005;111:3105–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

