Genome-wide association scan meta-analysis identifies three Loci influencing adiposity and fat distribution
- PMID: 19557161
- PMCID: PMC2695778
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000508
Genome-wide association scan meta-analysis identifies three Loci influencing adiposity and fat distribution
Erratum in
- PLoS Genet. 2009 Jul;5(7). doi: 10.1371/annotation/b6e8f9f6-2496-4a40-b0e3-e1d1390c1928 doi: 10.1371/annotation/b6e8f9f6-2496-4a40-b0e3-e1d1390c1928
Abstract
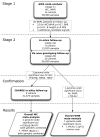
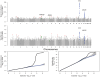
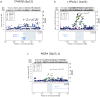
To identify genetic loci influencing central obesity and fat distribution, we performed a meta-analysis of 16 genome-wide association studies (GWAS, N = 38,580) informative for adult waist circumference (WC) and waist-hip ratio (WHR). We selected 26 SNPs for follow-up, for which the evidence of association with measures of central adiposity (WC and/or WHR) was strong and disproportionate to that for overall adiposity or height. Follow-up studies in a maximum of 70,689 individuals identified two loci strongly associated with measures of central adiposity; these map near TFAP2B (WC, P = 1.9x10(-11)) and MSRA (WC, P = 8.9x10(-9)). A third locus, near LYPLAL1, was associated with WHR in women only (P = 2.6x10(-8)). The variants near TFAP2B appear to influence central adiposity through an effect on overall obesity/fat-mass, whereas LYPLAL1 displays a strong female-only association with fat distribution. By focusing on anthropometric measures of central obesity and fat distribution, we have identified three loci implicated in the regulation of human adiposity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors from Decode Genetics Inc. own stocks and stock options in the company. VM, NL, KS and DMW are full-time employees of GlaxoSmithKline, a pharmaceutical company. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Pischon T, Boeing H, Hoffmann K, Bergmann M, Schulze MB, et al. General and abdominal adiposity and risk of death in Europe. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2105–2120. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet. 2005;366:1640–1649. - PubMed
-
- Baik I, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Giovannucci E, Spiegelman D, et al. Adiposity and mortality in men. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:264–271. - PubMed
-
- Kamel EG, McNeill G, Van Wijk MC. Usefulness of anthropometry and DXA in predicting intra-abdominal fat in obese men and women. Obes Res. 2000;8:36–42. - PubMed
-
- Schousboe K, Willemsen G, Kyvik KO, Mortensen J, Boomsma DI, et al. Sex differences in heritability of BMI: a comparative study of results from twin studies in eight countries. Twin Res. 2003;6:409–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G9521010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- GR076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK079466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 086596/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GR072960/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 DK080145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0801056/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DK067288/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002651/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GR069224/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- DK080145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK079466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK07191/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK067288/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL084729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G9521010D/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK029867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000649/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600717/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 064890/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 081682/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

