The dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker benidipine prevents lysophosphatidylcholine-induced endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta
- PMID: 19558657
- PMCID: PMC2710319
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-57
The dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker benidipine prevents lysophosphatidylcholine-induced endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta
Abstract
Background: Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), an atherogenic component of oxidized low-density lipoprotein, has been shown to induce the attenuation of endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation. Although benidipine, a dihydropyridine-calcium channel blocker, is known to have endothelial protective effects, the effects of benidipine on LPC-induced endothelial dysfunction remain unknown. We examined the effects of benidipine on the impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by LPC.
Methods: Benidipine was administered orally to rats and aortas were then isolated. Aortic rings were treated with LPC and endothelial functions were then evaluated. Additionally, the effects of benidipine on intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) and membrane fluidity altered by LPC in primary cultured rat aortic endothelial cells were examined. [Ca2+]i was measured using the fluorescent calcium indicator fura-2. Membrane fluidity was monitored by measuring fluorescence recovery after photobleaching.
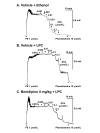
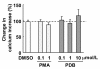
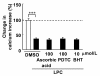
Results: Treatment with LPC impaired endothelial function. Benidipine prevents the impairment of relaxation induced by LPC. Acetylcholine elicited an increase in [Ca2+]i in fura-2 loaded endothelial cells. The increase in [Ca2+]i was suppressed after exposure to LPC. Plasma membrane fluidity increased following incubation with LPC. Benidipine inhibited the LPC-induced increase in membrane fluidity and impairment of increase in [Ca2+]i.
Conclusion: These results suggest that benidipine inhibited LPC-induced endothelial dysfunction by maintaining increase in [Ca2+]i. Benidipine possesses membrane stabilization properties in LPC-treated endothelial cells. It is speculated that the preservation of membrane fluidity by benidipine may play a role in the retainment of calcium mobilization. The present findings may provide new insights into the endothelial protective effects of benidipine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Benidipine, a dihydropyridine-calcium channel blocker, prevents lysophosphatidylcholine-induced injury and reactive oxygen species production in human aortic endothelial cells.Atherosclerosis. 2005 Jan;178(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.08.020. Atherosclerosis. 2005. PMID: 15585201
-
Benidipine, a dihydropyridine-calcium channel blocker, inhibits lysophosphatidylcholine-induced endothelial injury via stimulation of nitric oxide release.Pharmacol Res. 2006 Jan;53(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Pharmacol Res. 2006. PMID: 16172001
-
Effects of benidipine, a dihydropyridine-Ca2+ channel blocker, on expression of cytokine-induced adhesion molecules and chemoattractants in human aortic endothelial cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 13;498(1-3):303-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.086. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15364009
-
Pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, and clinical properties of benidipine hydrochloride, a novel, long-acting calcium channel blocker.J Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Apr;100(4):243-61. doi: 10.1254/jphs.dtj05001x. Epub 2006 Mar 25. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16565579 Review.
-
A new approach to the development of anti-ischemic drugs: protective drugs against cell injury induced by lysophosphatidylcholine.Life Sci. 1998;62(17-18):1695-9. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(98)00130-1. Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9585159 Review.
Cited by
-
Possible vasculoprotective role of linagliptin against sodium arsenite-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Feb;389(2):167-75. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1184-4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26497187
References
-
- Ylä-Herttuala S, Palinski W, Rosenfeld ME, Parthasarathy S, Carew TE, Butler S, Witztum JL, Steinberg D. Evidence for the presence of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbit and man. J Clin Invest. 1989;84:1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI114271. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miwa Y, Hirata K, Kawashima S, Akita H, Yokoyama M. Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization in intact endothelial cells of rabbit aorta. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:1561–1567. - PubMed
-
- Huang TY, Chen HI, Liu CY, Jen CJ. Lysophosphatidylcholine alters vascular tone in rat aorta by suppressing endothelial [Ca2+]i signaling. J Biomed Sci. 2002;9:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Kugiyama K, Ohgushi M, Sugiyama S, Murohara T, Fukunaga K, Miyamoto E, Yasue H. Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits surface receptor-mediated intracellular signals in endothelial cells by a pathway involving protein kinase C activation. Circ Res. 1992;71:1422–1428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

