Risk of lymphoma associated with combination anti-tumor necrosis factor and immunomodulator therapy for the treatment of Crohn's disease: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 19558997
- PMCID: PMC2846413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.01.004
Risk of lymphoma associated with combination anti-tumor necrosis factor and immunomodulator therapy for the treatment of Crohn's disease: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background & aims: Although anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy can effectively treat Crohn's disease (CD), there is concern that it might increase the risk of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). A meta-analysis was performed to determine the rate of NHL in adult CD patients who have received anti-TNF therapy and to compare this rate with that of a population-based registry and a population of CD patients treated with immunomodulators.
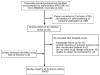
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Collaboration, and Web of Science were searched. Inclusion criteria included randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, or case series reporting on anti-TNF therapy in adult CD patients. Standardized incidence ratios (SIR) were calculated by comparing the pooled rate of NHL with the expected rate of NHL derived from the Surveillance Epidemiology & End Results (SEER) database and a meta-analysis of CD patients treated with immunomodulators.
Results: Twenty-six studies involving 8905 patients and 21,178 patient-years of follow-up were included. Among anti-TNF treated subjects, 13 cases of NHL were reported (6.1 per 10,000 patient-years). The majority of these patients had previous immunomodulator exposure. Compared with the expected rate of NHL in the SEER database (1.9 per 10,000 patient-years), anti-TNF treated subjects had a significantly elevated risk (SIR, 3.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-6.9). When compared with the NHL rate in CD patients treated with immunomodulators alone (4 per 10,000 patient-years), the SIR was 1.7 (95% confidence interval, 0.5-7.1).
Conclusions: The use of anti-TNF agents with immunomodulators is associated with an increased risk of NHL in adult CD patients, but the absolute rate of these events remains low and should be weighed against the substantial benefits associated with treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Insufficient evidence to conclude whether anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy increases the risk of lymphoma in Crohn's disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Oct;7(10):1139. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 May 22. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19465159 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kappelman MD, Rifas-Shiman SL, Kleinman K, et al. The prevalence and geographic distribution of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:1424–1429. - PubMed
-
- Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1541–1549. - PubMed
-
- Sands BE, Anderson FH, Bernstein CN, et al. Infliximab maintenance therapy for fistulizing Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:876–885. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Yan S, Bala M, et al. Infliximab maintenance treatment reduces hospitalizations, surgeries, and procedures in fistulizing Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:862–869. - PubMed
-
- Rutgeerts P, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Comparison of scheduled and episodic treatment strategies of infliximab in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:402–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

