Raptor binds the SAIN (Shc and IRS-1 NPXY binding) domain of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and regulates the phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 by mTOR
- PMID: 19561084
- PMCID: PMC2755659
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.027748
Raptor binds the SAIN (Shc and IRS-1 NPXY binding) domain of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and regulates the phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 by mTOR
Abstract
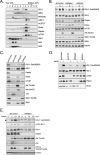
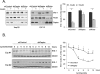
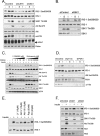
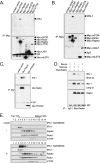
In normal physiological states mTOR phosphorylates and activates Akt. However, under diabetic-mimicking conditions mTOR inhibits phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase/Akt signaling by phosphorylating insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) at Ser-636/639. The molecular basis for the differential effect of mTOR signaling on Akt is poorly understood. Here, it has been shown that knockdown of mTOR, Raptor, and mLST8, but not Rictor and mSin1, suppresses insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 and stabilizes IRS-1 after long term insulin stimulation. This phosphorylation depends on the PI 3-kinase/PDK1 axis but is Akt-independent. At the molecular level, Raptor binds the SAIN (Shc and IRS-1 NPXY binding) domain of IRS-1 and regulates the phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 by mTOR. IRS-1 lacking the SAIN domain does not interact with Raptor, is not phosphorylated at Ser-636/639, and favorably interacts with PI 3-kinase. Overall, these data provide new insights in the molecular mechanisms by which mTORC1 inhibits PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling at the level of IRS-1 and suggest that mTOR signaling toward Akt is scaffold-dependent.
Figures

References
-
- Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., Sabatini D. M. (2005) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17,596–603 - PubMed
-
- Kim D. H., Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., King J. E., Latek R. R., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Sabatini D. M. (2002) Cell 110,163–175 - PubMed
-
- Hara K., Maruki Y., Long X., Yoshino K., Oshiro N., Hidayat S., Tokunaga C., Avruch J., Yonezawa K. (2002) Cell 110,177–189 - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov D. D., Guertin D. A., Ali S. M., Sabatini D. M. (2005) Science 307,1098–1101 - PubMed
-
- Guertin D. A., Stevens D. M., Thoreen C. C., Burds A. A., Kalaany N. Y., Moffat J., Brown M., Fitzgerald K. J., Sabatini D. M. (2006) Dev. Cell 11,859–871 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

