A discrete alcohol pocket involved in GIRK channel activation
- PMID: 19561601
- PMCID: PMC2717173
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2358
A discrete alcohol pocket involved in GIRK channel activation
Abstract
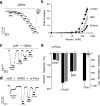
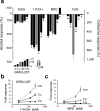
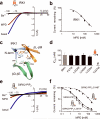
Ethanol modifies neural activity in the brain by modulating ion channels. Ethanol activates G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K(+) channels, but the molecular mechanism is not well understood. Here, we used a crystal structure of a mouse inward rectifier containing a bound alcohol and structure-based mutagenesis to probe a putative alcohol-binding pocket located in the cytoplasmic domains of GIRK channels. Substitutions with bulkier side-chains in the alcohol-binding pocket reduced or eliminated activation by alcohols. By contrast, alcohols inhibited constitutively open channels, such as IRK1 or GIRK2 engineered to strongly bind PIP(2). Mutations in the hydrophobic alcohol-binding pocket of these channels had no effect on alcohol-dependent inhibition, suggesting an alternate site is involved in inhibition. Comparison of high-resolution structures of inwardly rectifying K(+) channels suggests a model for activation of GIRK channels using this hydrophobic alcohol-binding pocket. These results provide a tool for developing therapeutic compounds that could mitigate the effects of alcohol.
Figures





References
-
- Cardoso RA, Brozowski SJ, Chavez-Noriega LE, Harpold M, Valenzuela CF, Harris RA. Effects of ethanol on recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;289:774–780. - PubMed
-
- Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF. Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989;243:1721–1724. - PubMed
-
- Mihic SJ, Ye Q, Wick MJ, Koltchine VV, Krasowski MD, Finn SE, Mascia MP, Valenzuela CF, Hanson KK, Greenblatt EP, Harris RA, Harrison NL. Sites of alcohol and volatile anaesthetic action on GABAA and glycine receptors. Nature. 1997;389:385–389. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Q, Lovinger DM. Pharmacologic characteristics of potentiation of 5-HT3 receptors by alcohols and diethyl ether in NCB-20 neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;278:732–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

