Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review
- PMID: 19561910
- PMCID: PMC2700454
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.39641
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: pathogenesis, clinical features, imaging and therapy review
Abstract
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) was first described in the early 1980s as a clinicopathologic syndrome characterized symptomatically by subacute or chronic respiratory illness and histopathologically by the presence of granulation tissue in the bronchiolar lumen, alveolar ducts and some alveoli, associated with a variable degree of interstitial and airspace infiltration by mononuclear cells and foamy macrophages. Persons of all ages can be affected. Dry cough and shortness of breath of 2 weeks to 2 months in duration usually characterizes BOOP. Symptoms persist despite antibiotic therapy. On imaging, air space consolidation can be indistinguishable from chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP), interstitial pneumonitis (acute, nonspecific and usual interstitial pneumonitis, neoplasm, inflammation and infection). The definitive diagnosis is achieved by tissue biopsy. Patients with BOOP respond favorably to treatment with steroids.
Keywords: Bronchiolitis; cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; organizing pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
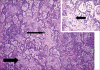
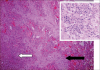
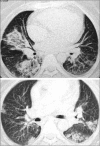



References
-
- Davison AG, Heard BE, McAllister WA, Turner-Warwick ME. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonitis. Q J Med. 1983;52:382–94. - PubMed
-
- Epler GR, Colby TV, McLoud TC, Carrington CB, Gaensler EA. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:152–8. - PubMed
-
- Wright JL, Cagle P, Churg A, Colby TV, Myers J. Diseases of the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146:240–62. - PubMed
-
- Lohr RH, Boland BJ, Douglas WW, Dockrell DH, Colby TV, Swensen SJ, et al. Organizing pneumonia: Features and prognosis of cryptogenic, secondary and focal variants. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:1323–9. - PubMed
-
- Colby TV. Bronchiolitis. Pathologic considerations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;109:101–9. - PubMed

