Obstetric brachial plexus palsy: treatment strategy, long-term results, and prognosis
- PMID: 19562016
- PMCID: PMC2695299
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0083
Obstetric brachial plexus palsy: treatment strategy, long-term results, and prognosis
Abstract
Background: Obstetric brachial plexus palsy is rare, but the limb impairments are manifold and often long-lasting. Physiotherapy, microsurgical nerve reconstruction, secondary joint corrections, and muscle transpositions are employed with success. The role of conservative and operative treatment options should be regularly reviewed.
Methods: Selective literature review (evidence levels 3 and 4) and analysis of personal clinical operative and scientific experience over the past 15 years.
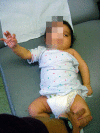
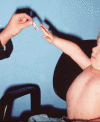
Results: Children with upper and total plexus palsy displaying nerve root avulsions and/or -ruptures are treated today by early primary nerve reconstruction in the first few months of life followed by secondary corrections, with good functional results. The late complications, with muscle weakness, impaired motion patterns, and joint dysplasia, are often underrated.
Conclusions: The potential for scientific analysis is limited, due to the rarity and interindividual variability of the lesions and the varying effects on function and growth. Expectations and compliance are different in every patient. Surgical techniques are not yet standardized. Knowledge of the consequences for joint growth and congruence is inadequate. Today, functional improvement can be achieved by surgery in most clinical manifestations of obstetric brachial plexus palsy, within the framework of an interdisciplinary treatment concept.
Keywords: microsurgery; nerve lesion; neurosurgery; obstetrics; trauma.
Figures


References
-
- Bahm J. Die kindliche Armplexusparese—Übersicht zur Klinik, Pathophysiologie und chirurgischen Behandlungsstrategie. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2003;35:83–97. - PubMed
-
- Bahm J. Die kindliche Armplexusparese—Eine aktuelle Übersicht sekundärer Operationsverfahren. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2004;36:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Antoniadis G, König RW, Mohr K, Kretschmer T, Richter HP. Management bei geburtstraumatischen Läsionen des Plexus brachialis—Eigene Erfahrungen mit der primären operativen Behandlung. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2003;35:98–105. - PubMed
-
- Heilmann A, Krishnan KG, Heubner G, Pinzer Th, Schackert G, Gahr M. Therapeutisches Vorgehen bei geburtstraumatischer Plexus-brachialis-Läsion. Ärzteblatt Sachsen. 2003;9:423–426.
-
- Strömbeck C, Krumlinde-Sundholm L, Remahl S, Sejersen T. Long-term follow-up of children with obstetric brachial plexus palsy I: functional aspects. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;49:198–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

