Declining semen quality among south Indian infertile men: A retrospective study
- PMID: 19562058
- PMCID: PMC2700673
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-1208.38972
Declining semen quality among south Indian infertile men: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Male reproductive function has recently attracted increasing attention due to reports on time-related decline in semen quality. Furthermore, regional differences in the semen quality have also been reported.
Aim: To investigate the semen quality among large cohort of infertile individuals at a regional level, in terms of the sperm concentration, total sperm motility, sperm morphology and incidence of azoospermia over a period of 13 years.
Setting: University infertility clinic at Kasturba Hospital, Manipal which is a tertiary healthcare centre serving the general population.
Design: Retrospective analysis.
Materials and methods: This includes a total of 7770 subjects who presented for semen analysis from 1993 to 2005. The data regarding ejaculate volume, sperm density, motility, morphology and the incidence of azoospermia were collected.
Statistical analysis used: One way analysis of variance (ANOVA), regression analysis and Chi square analysis.
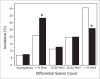
Results: The average sperm density among infertile men during 2004-2005 was 26.61 +/- 0.71 millions/mL which was significantly lower than the average sperm density observed in 1993-1994 (38.18 +/- 1.46 millions/mL). Similar trend was also observed for sperm motility (47.14% motile sperms vs. 61.16%) and normal sperm morphology (19.75% vs. 40.51%). Interestingly, the incidence of severe oligospermia (mean sperm density <10 millions/mL) observed in 2002-2005 and 1993-1997 demonstrated a significant inverse relationship (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our study provides the first evidence that the quality of human semen evaluated for infertility is deteriorating in the southern part of the India over the years, probably due to environmental, nutritional, life style or socioeconomic causes.
Keywords: Azoospermia; infertility; reproductive function; semen quality; seminal parameters; sperm concentration; sperm decline; spermatozoa.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Auger J, Kunstmann JM, Czyglik F, Jouannet P. Decline in semen quality among fertile men in Paris during the past 20 years. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:281–5. - PubMed
-
- Lackner J, Schatzl G, Waldhor T, Resch K, Kratzik C, Marberger M. Constant decline in sperm concentration in infertile males in an urban population: Experience over 18 years. Fertil Steril. 2005;84:1657–61. - PubMed
-
- Marimuthu P, Kapilashrami MC, Misro MM, Singh G. Evaluation of trend in semen analysis for 11 years in subjects attending a fertility clinic in India. Asian J Androl. 2003;5:221–5. - PubMed
-
- Fisch H, Goluboff ET, Olson JH, Feldshuh J, Broder SJ, Barad DH. Semen analyses in 1,283 men from the United States over a 25-year period: No decline in quality. Fertil Steril. 1996;65:1009–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources