Phase II trials of erlotinib or gefitinib in patients with recurrent meningioma
- PMID: 19562255
- PMCID: PMC3786190
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-009-9948-7
Phase II trials of erlotinib or gefitinib in patients with recurrent meningioma
Abstract
There are no established treatments for recurrent meningioma when surgical and radiation options are exhausted. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is often over-expressed in meningiomas and may promote tumor growth. In open label, single arm phase II studies of the EGFR inhibitors gefitinib (NABTC 00-01) and erlotinib (NABTC 01-03) for recurrent malignant gliomas, we included exploratory subsets of recurrent meningioma patients. We have pooled the data and report the results here. Patients with recurrent histologically confirmed meningiomas with no more than 2 previous chemotherapy regimens were treated with gefitinib 500 mg/day or erlotinib 150 mg/day until tumor progression or unacceptable toxicity. Twenty-five eligible patients were enrolled with median age 57 years (range 29-81) and median Karnofsky performance status (KPS) score 90 (range 60-100). Sixteen patients (64%) received gefitinib and 9 (36%) erlotinib. Eight patients (32%) had benign tumors, 9 (36%) atypical, and 8 (32%) malignant. For benign tumors, the 6-month progression-free survival (PFS6) was 25%, 12-month PFS (PFS12) 13%, 6-month overall survival (OS6) 63%, and 12-month OS (OS12) 50%. For atypical and malignant tumors, PFS6 was 29%, PFS12 18%, OS6 71%, and OS12 65%. The PFS and OS were not significantly different by histology. There were no objective imaging responses, but 8 patients (32%) maintained stable disease. Although treatment was well-tolerated, neither gefitinib nor erlotinib appear to have significant activity against recurrent meningioma. The role of EGFR inhibitors in meningiomas is unclear. Evaluation of multi-targeted inhibitors and EGFR inhibitors in combination with other targeted molecular agents may be warranted.
Figures
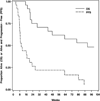
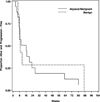

References
-
- CBTRUS. Statistical Report: Primary Brain Tumors in the United States, 2000–2004. Published by the Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States. 2008
-
- Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Budka H. Meningeal tumors. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK, editors. WHO Classification of Tumors Tumors of the Nervous System. Lyon: IARC; pp. 175–196.
-
- Lamszus K. Meningioma pathology, genetics, and biology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Perry A, Gutmann DH, Reifenberger G. Molecular pathogenesis of meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2004;70:183–202. - PubMed
-
- McMullen KP, Stieber VW. Meningioma: current treatment options and future directions. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2004;5:499–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01-RR0865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62407-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-U01CA62399-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62421-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA62412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA62399/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR003186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062405/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA062412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA62405/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR03186/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

