Molecular genetic analysis of podocyte genes in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis--a review
- PMID: 19562370
- PMCID: PMC2745545
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-009-1017-x
Molecular genetic analysis of podocyte genes in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis--a review
Abstract
This review deals with podocyte proteins that play a significant role in the structure and function of the glomerular filter. Genetic linkage studies has identified several genes involved in the development of nephrotic syndrome and contributed to the understanding of the pathophysiology of glomerular proteinuria and/or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Here, we describe already well-characterized genetic diseases due to mutations in nephrin, podocin, CD2AP, alpha-actinin-4, WT1, and laminin beta2 chain, as well as more recently identified genetic abnormalities in TRPC6, phospholipase C epsilon, and the proteins encoded by the mitochondrial genome. In addition, the role of the proteins which have shown to be important for the structure and functions by gene knockout studies in mice, are also discussed. Furthermore, some rare syndromes with glomerular involvement, in which molecular defects have been recently identified, are briefly described. In summary, this review updates the current knowledge of genetic causes of congenital and childhood nephrotic syndrome and provides new insights into mechanisms of glomerular dysfunction.
Figures
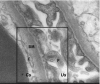

 negatively charged glycogalyx. Modified from [86], with permission
negatively charged glycogalyx. Modified from [86], with permissionReferences
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17152860', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17152860/'}]}
- Agarwal AK, Zhou XJ, Hall RK et al (2006) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in patients with mandibuloacral dysplasia owing to ZMPSTE24 deficiency. J Investig Med 54:208–13 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1558084', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1558084/'}]}
- Artero M, Biava C, Amend W et al (1992) Recurrent focal glomerulosclerosis: natural history and response to therapy. Am J Med 92:375–383 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8154495', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8154495/'}]}
- Artero ML, Sharma R, Savin VJ, Vincenti F (1994) Plasmapheresis reduces proteinuria and serum capacity to injure glomeruli in patients with recurrent focal glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis 23:574–581 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15840009', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15840009/'}]}
- Ballermann BJ (2005) Glomerular endothelial cell differentiation. Kidney Int 67:1668–1671 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18424452', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18424452/'}]}
- Balreira A, Gaspar P, Caiola D et al (2008) A nonsense mutation in the LIMP-2 gene associated with progressive myoclonic epilepsy and nephrotic syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 17:2238–2243 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

