Myofibrillar myopathies: a clinical and myopathological guide
- PMID: 19563540
- PMCID: PMC8094720
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00289.x
Myofibrillar myopathies: a clinical and myopathological guide
Abstract
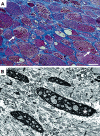
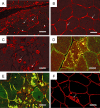
Myofibrillar myopathies (MFMs) are histopathologically characterized by desmin-positive protein aggregates and myofibrillar degeneration. Because of the marked phenotypic and pathomorphological variability, establishing the diagnosis of MFM can be a challenging task. While MFMs are partly caused by mutations in genes encoding for extramyofibrillar proteins (desmin, alphaB-crystallin, plectin) or myofibrillar proteins (myotilin, Z-band alternatively spliced PDZ-containing protein, filamin C, Bcl-2-associated athanogene-3, four-and-a-half LIM domain 1), a large number of these diseases are caused by still unresolved gene defects. Although recent years have brought new insight into the pathogenesis of MFMs, the precise molecular pathways and sequential steps that lead from an individual gene defect to progressive muscle damage are still unclear. This review focuses on the clinical and myopathological aspects of genetically defined MFMs, and shall provide a diagnostic guide for this numerically significant group of protein aggregate myopathies.
Figures





References
-
- Bär H, Fischer D, Goudeau B, Kley RA, Clemen CS, Vicart P et al (2005) Pathogenic effects of a novel heterozygous r350p desmin mutation on the assembly of desmin intermediate filaments in vivo and in vitro . Hum Mol Genet 14:1251–1260. - PubMed
-
- Bär H, Kostareva A, Sjöberg G, Sejersen T, Katus HA, Herrmann H (2006) Forced expression of desmin and desmin mutants in cultured cells: impact of myopathic missense mutations in the central coiled‐coil domain on network formation. Exp Cell Res 312:1554–1565. - PubMed
-
- Bär H, Goudeau B, Walde S, Casteras‐Simon M, Mücke N, Shatunov A et al (2007) Conspicuous involvement of desmin tail mutations in diverse cardiac and skeletal myopathies. Hum Mutat 28:374–386. - PubMed
-
- Bär H, Mücke N, Katus HA, Aebi U, Herrmann H (2007) Assembly defects of desmin disease mutants carrying deletions in the alpha‐helical rod domain are rescued by wild type protein. J Struct Biol 158:107–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

