Isolation of a human-like antibody fragment (scFv) that neutralizes ricin biological activity
- PMID: 19563687
- PMCID: PMC2716335
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-60
Isolation of a human-like antibody fragment (scFv) that neutralizes ricin biological activity
Abstract
Background: Ricin is a lethal toxin that inhibits protein synthesis. It is easily extracted from a ubiquitously grown plant, Ricinus communis, and thus readily available for use as a bioweapon (BW). Anti-ricin antibodies provide the only known therapeutic against ricin intoxication.
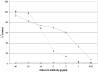
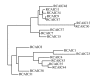
Results: In this study, after immunizing a non-human primate (Macaca fascicularis) with the ricin chain A (RTA), a phage-displayed immune library was built (2 x 108 clones), that included the lambda light chain fragment. The library was screened against ricin, and specific binders were sequenced and further analyzed. The best clone, 43RCA, was isolated using a new, stringent neutralization test. 43RCA had a high, picomolar affinity (41 pM) and neutralized ricin efficiently (IC50 = 23 +/- 3 ng/ml, corresponding to a [scFv]/[ricin] molar ratio of 4). The neutralization capacity of 43RCA compared favourably with that of polyclonal anti-deglycosylated A chain (anti-dgRCA) IgGs, obtained from hyperimmune mouse serum, which were more efficient than any monoclonal at our disposal. The 43RCA sequence is very similar to that for human IgG germline genes, with 162 of 180 identical amino acids for the VH and VL (90% sequence identity).
Conclusion: Results of the characterization studies, and the high degree of identity with human germline genes, altogether make this anti-ricin scFv, or an IgG derived from it, a likely candidate for use in humans to minimize effects caused by ricin intoxication.
Figures


References
-
- Olsnes S, Pihl A. Ricin – a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1972;20:327–329. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:8128–8130. - PubMed
-
- Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin poisoning: a comprehensive review. Jama. 2005;294:2342–2351. - PubMed
-
- Balint GA. Ricin: the toxic protein of castor oil seeds. Toxicology. 1974;2:77–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

