Demonstration of catch bonds between an integrin and its ligand
- PMID: 19564406
- PMCID: PMC2712956
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200810002
Demonstration of catch bonds between an integrin and its ligand
Abstract
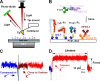
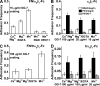
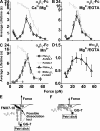
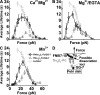
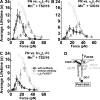
Binding of integrins to ligands provides anchorage and signals for the cell, making them prime candidates for mechanosensing molecules. How force regulates integrin-ligand dissociation is unclear. We used atomic force microscopy to measure the force-dependent lifetimes of single bonds between a fibronectin fragment and an integrin alpha(5)beta(1)-Fc fusion protein or membrane alpha(5)beta(1). Force prolonged bond lifetimes in the 10-30-pN range, a counterintuitive behavior called catch bonds. Changing cations from Ca(2+)/Mg(2+) to Mg(2+)/EGTA and to Mn(2+) caused longer lifetime in the same 10-30-pN catch bond region. A truncated alpha(5)beta(1) construct containing the headpiece but not the legs formed longer-lived catch bonds that were not affected by cation changes at forces <30 pN. Binding of monoclonal antibodies that induce the active conformation of the integrin headpiece shifted catch bonds to a lower force range. Thus, catch bond formation appears to involve force-assisted activation of the headpiece but not integrin extension.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

