Signal transduction cross talk mediated by Jun N-terminal kinase-interacting protein and insulin receptor substrate scaffold protein complexes
- PMID: 19564410
- PMCID: PMC2725725
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00155-09
Signal transduction cross talk mediated by Jun N-terminal kinase-interacting protein and insulin receptor substrate scaffold protein complexes
Abstract
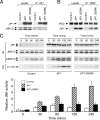
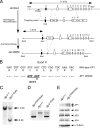
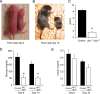
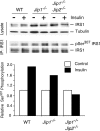
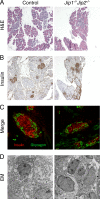
Scaffold proteins have been established as important mediators of signal transduction specificity. The insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins represent a critical group of scaffold proteins that are required for signal transduction by the insulin receptor, including the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting proteins (JIPs) represent a different group of scaffold molecules that are implicated in the regulation of the JNK. These two signaling pathways are functionally linked because JNK can phosphorylate IRS1 on the negative regulatory site Ser-307. Here we demonstrate the physical association of these signaling pathways using a proteomic approach that identified insulin-regulated complexes of JIPs together with IRS scaffold proteins. Studies using mice with JIP scaffold protein defects confirm that the JIP1 and JIP2 proteins are required for normal glucose homeostasis. Together, these observations demonstrate that JIP proteins can influence insulin-stimulated signal transduction mediated by IRS proteins.
Figures



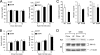
Similar articles
-
Requirement of JIP1-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation for obesity-induced insulin resistance.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(19):4616-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00585-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20679483 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-2 by glycogen synthase kinase-3 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase plays a role in hepatic insulin signaling.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Feb;294(2):E307-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00534.2007. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18029441
-
Dissociation of Akt1 from its negative regulator JIP1 is mediated through the ASK1-MEK-JNK signal transduction pathway during metabolic oxidative stress: a negative feedback loop.J Cell Biol. 2005 Jul 4;170(1):61-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200502070. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15998799 Free PMC article.
-
[Elucidation of a New Mechanism of Onset of Insulin Resistance: Effects of Statins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α on Insulin Signal Transduction].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(11):1329-1334. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00116. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30381640 Review. Japanese.
-
The role of scaffold proteins in JNK signalling.Cell Prolif. 2010 Feb;43(1):56-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2009.00654.x. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Cell Prolif. 2010. PMID: 19922489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic syndrome exacerbates amyloid pathology in a comorbid Alzheimer's mouse model.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Oct 1;1866(10):165849. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165849. Epub 2020 May 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32485218 Free PMC article.
-
A Protein Scaffold Coordinates SRC-Mediated JNK Activation in Response to Metabolic Stress.Cell Rep. 2017 Sep 19;20(12):2775-2783. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.025. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28930674 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Silencing of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 8 Interacting Protein-1 Conferred Its Role in Pancreatic β-Cell Physiology and Insulin Secretion.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 20;13(2):307. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020307. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837926 Free PMC article.
-
PKIS: computational identification of protein kinases for experimentally discovered protein phosphorylation sites.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Aug 13;14:247. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-247. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23941207 Free PMC article.
-
Mining for Candidate Genes Related to Pancreatic Cancer Using Protein-Protein Interactions and a Shortest Path Approach.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:623121. doi: 10.1155/2015/623121. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26613085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, H., K. Murao, H. Imachi, W. M. Cao, X. Yu, K. Yoshida, N. C. Wong, M. A. Shupnik, J. A. Haefliger, G. Waeber, and T. Ishida. 2004. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated thyrotropin expression involves islet-brain-1/c-Jun N-terminal kinase interacting protein-1. Endocrinology 1455623-5628. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre, V., T. Uchida, L. Yenush, R. Davis, and M. F. White. 2000. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 2759047-9054. - PubMed
-
- Allaman-Pillet, N., J. Storling, A. Oberson, R. Roduit, S. Negri, C. Sauser, P. Nicod, J. S. Beckmann, D. F. Schorderet, T. Mandrup-Poulsen, and C. Bonny. 2003. Calcium- and proteasome-dependent degradation of the JNK scaffold protein islet-brain 1. J. Biol. Chem. 27848720-48726. - PubMed
-
- Bauman, A. L., A. S. Goehring, and J. D. Scott. 2004. Orchestration of synaptic plasticity through AKAP signaling complexes. Neuropharmacology 46299-310. - PubMed
-
- Bonny, C., P. Nicod, and G. Waeber. 1998. IB1, a JIP-1-related nuclear protein present in insulin-secreting cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2731843-1846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
