Effect of heart rate and coronary calcification on the diagnostic accuracy of the dual-source CT coronary angiography in patients with suspected coronary artery disease
- PMID: 19568462
- PMCID: PMC2702043
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.4.347
Effect of heart rate and coronary calcification on the diagnostic accuracy of the dual-source CT coronary angiography in patients with suspected coronary artery disease
Abstract
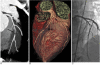
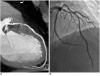
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of a dual-source computed tomography (DSCT) coronary angiography, with a particular focus on the effect of heart rate and calcifications.
Materials and methods: One hundred and nine patients with suspected coronary disease were divided into 2 groups according to a mean heart rate (< 70 bpm and >or= 70 bpm) and into 3 groups according to the mean Agatston calcium scores (<or= 100, 101-400, and > 400). Next, the effect of heart rate and calcification on the accuracy of coronary artery stenosis detection was analyzed by using an invasive coronary angiography as a reference standard. Coronary segments of less than 1.5 mm in diameter in an American Heart Association (AHA) 15-segment model were independently assessed.
Results: The mean heart rate during the scan was 71.8 bpm, whereas the mean Agatston score was 226.5. Of the 1,588 segments examined, 1,533 (97%) were assessable. A total of 17 patients had calcium scores above 400 Agatston U, whereas 50 had heart rates >or= 70 bpm. Overall the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive values (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV) for significant stenoses were: 95%, 91%, 65%, and 99% (by segment), respectively and 97%, 90%, 81%, and 91% (by artery), respectively (n = 475). Heart rate showed no significant impact on lesion detection; however, vessel calcification did show a significant impact on accuracy of assessment for coronary segments. The specificity, PPV and accuracy were 96%, 80%, and 96% (by segment), respectively for an Agatston score less than 100% and 99%, 96% and 98% (by artery). For an Agatston score of greater to or equal to 400 the specificity, PPV and accuracy were reduced to 79%, 55%, and 83% (by segment), respectively and to 79%, 69%, and 85% (by artery), respectively.
Conclusion: The DSCT provides a high rate of accuracy for the detection of significant coronary artery disease, even in patients with high heart rates and evidence of coronary calcification. However, patients with severe coronary calcification (> 400 U) remain a challenge to diagnose.
Keywords: Coronary angiography; Coronary artery disease; Dual-source computed tomography.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of dual-source CT coronary angiography: First experience in a high pre-test probability population without heart rate control.Eur Radiol. 2006 Dec;16(12):2739-47. doi: 10.1007/s00330-006-0474-0. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Eur Radiol. 2006. PMID: 17031451 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of dual-source CT coronary angiography in a population unselected for degree of coronary artery calcification and without heart rate modification.Clin Radiol. 2010 Feb;65(2):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2009.09.012. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Clin Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20103432
-
Dual-source CT: effect of heart rate, heart rate variability, and calcification on image quality and diagnostic accuracy.Radiology. 2008 May;247(2):346-55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2472070906. Epub 2008 Mar 27. Radiology. 2008. PMID: 18372455
-
Diagnostic accuracy of first generation dual-source computed tomography in the assessment of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis from 24 studies.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Jul;27(6):755-71. doi: 10.1007/s10554-010-9690-4. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20857200 Review.
-
Coronary artery calcium scoring and its impact on the clinical practice in the era of multidetector CT.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Dec;27 Suppl 1:9-25. doi: 10.1007/s10554-011-9964-5. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 22012492 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of age and plaque morphology on diagnostic accuracy of dual source multidetector computed tomography coronary angiography.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2014 Jun;11(2):106-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5411.2014.02.013. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25009559 Free PMC article.
-
Salusin-β is superior to salusin-α as a marker for evaluating coronary atherosclerosis.J Int Med Res. 2020 Feb;48(2):300060520903868. doi: 10.1177/0300060520903868. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32054363 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography for stenosis detection according to calcium score: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2012 Dec;22(12):2688-98. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2551-x. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Eur Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22797978
-
Calcium scoring: a personalized probability assessment predicts the need for additional or alternative testing to coronary CT angiography.Eur Radiol. 2020 Oct;30(10):5499-5506. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06921-7. Epub 2020 May 13. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32405749 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of conventional scoring systems to machine learning models for the prediction of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing coronary computed tomography angiography.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 26;9:994483. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.994483. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36386332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohnesorge B, Flohr T, Becker C, Kopp AF, Schoepf UJ, Baum U, et al. Cardiac imaging by means of electrocardiographically gated multisection spiral CT: initial experience. Radiology. 2000;217:564–571. - PubMed
-
- Kachelriess M, Ulzheimer S, Kalender WA. ECG-correlated image reconstruction from subsecond multi-slice spiral CT scans of the heart. Med Phys. 2000;27:1881–1902. - PubMed
-
- Taguchi K, Anno H. High temporal resolution for multislice helical computed tomography. Med Phys. 2000;27:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Becker CR, Knez A, Leber A, Hong C, Treede H, Wildhirt S, et al. Initial experiences with multislice detector spiral CT in diagnosis of arteriosclerosis of coronary vessels. Radiologe. 2000;40:118–122. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach S, Ulzheimer S, Baum U, Kachelriess M, Ropers D, Giesler T, et al. Noninvasive coronary angiography by retrospectively ECG-gated multislice spiral CT. Circulation. 2000;102:2823–2828. - PubMed

