Hygromorphs: from pine cones to biomimetic bilayers
- PMID: 19570796
- PMCID: PMC2838359
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0184
Hygromorphs: from pine cones to biomimetic bilayers
Abstract
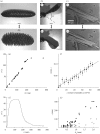
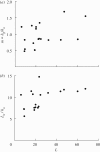
We consider natural and artificial hygromorphs, objects that respond to environmental humidity by changing their shape. Using the pine cone as an example that opens when dried and closes when wet, we quantify the geometry, mechanics and dynamics of closure and opening at the cell, tissue and organ levels, building on our prior structural knowledge. A simple scaling theory allows us to quantify the hysteretic dynamics of opening and closing. We also show how simple bilayer hygromorphs of paper and polymer show similar behaviour that can be quantified via a theory which couples fluid transport in a porous medium and evaporative flux to mechanics and geometry. Our work unifies varied observations of natural hygromorphs and suggests interesting biomimetic analogues, which we illustrate using an artificial flower with a controllable blooming and closing response.
Figures



References
-
- Arnold W. 1899. The cord moss and its allies. Bryologist 2, 52–55.
-
- Bell J. M., Cameron F. K. 1906. The flow of liquids through capillary spaces. J. Phys. Chem. 10, 658–674. (10.1021/j150080a005) - DOI
-
- Dawson C., Vincent J. F. V., Rocca A.-M. 1997. How pine cones open. Nature 390, 668 (10.1038/37745) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

