Parallel functional activity profiling reveals valvulopathogens are potent 5-hydroxytryptamine(2B) receptor agonists: implications for drug safety assessment
- PMID: 19570945
- PMCID: PMC2769050
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.058057
Parallel functional activity profiling reveals valvulopathogens are potent 5-hydroxytryptamine(2B) receptor agonists: implications for drug safety assessment
Abstract
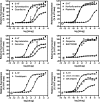
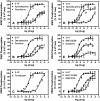
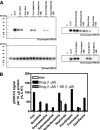
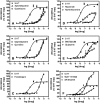
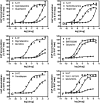
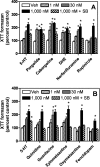
Drug-induced valvular heart disease (VHD) is a serious side effect of a few medications, including some that are on the market. Pharmacological studies of VHD-associated medications (e.g., fenfluramine, pergolide, methysergide, and cabergoline) have revealed that they and/or their metabolites are potent 5-hydroxytryptamine(2B) (5-HT(2B)) receptor agonists. We have shown that activation of 5-HT(2B) receptors on human heart valve interstitial cells in vitro induces a proliferative response reminiscent of the fibrosis that typifies VHD. To identify current or future drugs that might induce VHD, we screened approximately 2200 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved or investigational medications to identify 5-HT(2B) receptor agonists, using calcium-based high-throughput screening. Of these 2200 compounds, 27 were 5-HT(2B) receptor agonists (hits); 14 of these had previously been identified as 5-HT(2B) receptor agonists, including seven bona fide valvulopathogens. Six of the hits (guanfacine, quinidine, xylometazoline, oxymetazoline, fenoldopam, and ropinirole) are approved medications. Twenty-three of the hits were then "functionally profiled" (i.e., assayed in parallel for 5-HT(2B) receptor agonism using multiple readouts to test for functional selectivity). In these assays, the known valvulopathogens were efficacious at concentrations as low as 30 nM, whereas the other compounds were less so. Hierarchical clustering analysis of the pEC(50) data revealed that ropinirole (which is not associated with valvulopathy) was clearly segregated from known valvulopathogens. Taken together, our data demonstrate that patterns of 5-HT(2B) receptor functional selectivity might be useful for identifying compounds likely to induce valvular heart disease.
Figures


References
-
- Bourdon DM, Wing MR, Edwards EB, Sondek J, Harden TK. (2006) Quantification of isozyme-specific activation of phospholipase C-beta2 by Rac GTPases and phospholipase C-epsilon by Rho GTPases in an intact cell assay system. Methods Enzymol 406:489–499 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254 - PubMed
-
- Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, Schaff HV. (1997) Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine-phentermine. N Engl J Med 337:581–588 - PubMed
-
- Droogmans S, Cosyns B, D'haenen H, Creeten E, Weytjens C, Franken PR, Scott B, Schoors D, Kemdem A, Close L, et al. (2007) Possible association between 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine abuse and valvular heart disease. Am J Cardiol 100:1442–1445 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

