M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 19571279
- PMCID: PMC2762083
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810457
M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic membranous nephropathy, a common form of the nephrotic syndrome, is an antibody-mediated autoimmune glomerular disease. Serologic diagnosis has been elusive because the target antigen is unknown.
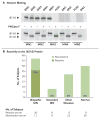
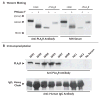
Methods: We performed Western blotting of protein extracts from normal human glomeruli with serum samples from patients with idiopathic or secondary membranous nephropathy or other proteinuric or autoimmune diseases and from normal controls. We used mass spectrometry to analyze the reactive protein bands and confirmed the identity and location of the target antigen with a monospecific antibody.
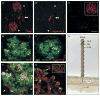
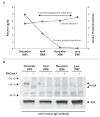
Results: Serum samples from 26 of 37 patients (70%) with idiopathic but not secondary membranous nephropathy specifically identified a 185-kD glycoprotein in nonreduced glomerular extract. Mass spectrometry of the reactive protein band detected the M-type phospholipase A(2) receptor (PLA(2)R). Reactive serum specimens recognized recombinant PLA(2)R and bound the same 185-kD glomerular protein as did the monospecific anti-PLA(2)R antibody. Anti-PLA(2)R autoantibodies in serum samples from patients with membranous nephropathy were mainly IgG4, the predominant immunoglobulin subclass in glomerular deposits. PLA(2)R was expressed in podocytes in normal human glomeruli and colocalized with IgG4 in immune deposits in glomeruli of patients with membranous nephropathy. IgG eluted from such deposits in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy, but not in those with lupus membranous or IgA nephropathy, recognized PLA(2)R.
Conclusions: A majority of patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy have antibodies against a conformation-dependent epitope in PLA(2)R. PLA(2)R is present in normal podocytes and in immune deposits in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy, indicating that PLA(2)R is a major antigen in this disease.
2009 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures


Comment in
-
Human idiopathic membranous nephropathy--a mystery solved?N Engl J Med. 2009 Jul 2;361(1):81-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0903343. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19571287 No abstract available.
-
First identification of an antigen in autoimmune idiopathic membranous nephropathy: toward targeted therapy?Am J Kidney Dis. 2010 May;55(5):820-3. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.09.017. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010. PMID: 19926373 No abstract available.
References
-
- Van Damme BJ, Fleuren GJ, Bakker WW, Vernier RL, Hoedemaeker PJ. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978;38:502–10. - PubMed
-
- Couser WG, Salant DJ. In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1980;17:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
