A new method for measurement of total plasma PCSK9: clinical applications
- PMID: 19571328
- PMCID: PMC2789774
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M900273-JLR200
A new method for measurement of total plasma PCSK9: clinical applications
Abstract
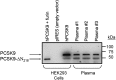
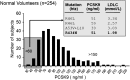
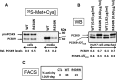
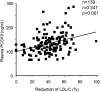
The proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin-9 (PCSK9) circulates in plasma as mature and furin-cleaved forms. A polyclonal antibody against human PCSK9 was used to develop an ELISA that measures total plasma PCSK9 rather than only the mature form. A cross-sectional study evaluated plasma levels in normal (n = 254) and hypercholesterolemic (n = 200) subjects treated or untreated with statins or statin plus ezetimibe. In controls, mean plasma PCSK9 (89.5 +/- 31.9 ng/ml) correlated positively with age, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides, and fasting glucose. Sequencing PCSK9 from individuals at the extremes of the normal PCSK9 distribution identified a new loss-of-function R434W variant associated with lower levels of circulating PCSK9 and LDL-C. In hypercholesterolemic subjects, PCSK9 levels were higher than in controls (99.3 +/- 31.7 ng/ml, P < 0.04) and increased in proportion to the statin dose, combined or not with ezetimibe. In treated patients (n = 139), those with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH; due to LDL receptor gene mutations) had higher PCSK9 values than non-FH (147.01 +/- 42.5 vs. 127.2 +/- 40.8 ng/ml, P < 0.005), but LDL-C reduction correlated positively with achieved plasma PCSK9 levels to a similar extent in both subsets (r = 0.316, P < 0.02 in FH and r = 0.275, P < 0.009 in non-FH). The detection of circulating PCSK9 in both FH and non-FH subjects means that this assay could be used to monitor response to therapy in a wide range of patients.
Figures


References
-
- Goldstein J. L., Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S. Familial hypercholesterolemia. 2001. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. Valle D., Scriver C. R., Beaudet A. L., Sly W. S., Childs B., Volgestein B., editors. Chapter 120, 8th edition McGraw Hill, New York: 2863–2913.
-
- Abifadel M., Varret M., Rabes J. P., Allard D., Ouguerram K., Devillers M., Cruaud C., Benjannet S., Wickham L., Erlich D., et al. 2003. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 34: 154–156. - PubMed
-
- Seidah N. G., Benjannet S., Wickham L., Marcinkiewicz J., Jasmin S. B., Stifani S., Basak A., Prat A., Chretien M. 2003. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100: 928–933. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seidah N. G., Prat A. 2007. The proprotein convertases are potential targets in the treatment of dyslipidemia. J. Mol. Med. 85: 685–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

