Systematic evaluation of drug-disease relationships to identify leads for novel drug uses
- PMID: 19571805
- PMCID: PMC2836384
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2009.103
Systematic evaluation of drug-disease relationships to identify leads for novel drug uses
Abstract
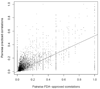
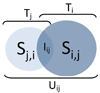
Drug repositioning refers to the discovery of alternative uses for drugs--uses that are different from that for which the drugs were originally intended. One challenge in this effort lies in choosing the indication for which a drug of interest could be prospectively tested. We systematically evaluated a drug treatment-based view of diseases in order to address this challenge. Suggestions for novel drug uses were generated using a "guilt by association" approach. When compared with a control group of drug uses, the suggested novel drug uses generated by this approach were significantly enriched with respect to previous and ongoing clinical trials.
Figures
References
-
- Scheindlin S. Rare diseases, orphan drugs, and orphaned patients. Molecular interventions. 2006 Aug;6(4):186–191. - PubMed
-
- Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, et al. Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide. The New England journal of medicine. 1998 Nov 5;339(19):1341–1348. - PubMed
-
- Singhal S, Mehta J, Desikan R, Ayers D, Roberson P, Eddlemon P, et al. Antitumor activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple myeloma. The New England journal of medicine. 1999 Nov 18;341(21):1565–1571. - PubMed
-
- Ashburn TT, Thor KB. Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nature reviews. 2004 Aug;3(8):673–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

