Evidence of Xist RNA-independent initiation of mouse imprinted X-chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 19571810
- PMCID: PMC2754729
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08161
Evidence of Xist RNA-independent initiation of mouse imprinted X-chromosome inactivation
Abstract
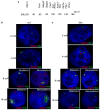
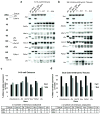
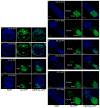
XX female mammals undergo transcriptional silencing of most genes on one of their two X chromosomes to equalize X-linked gene dosage with XY males in a process referred to as X-chromosome inactivation (XCI). XCI is an example of epigenetic regulation. Once enacted in individual cells of the early female embryo, XCI is stably transmitted such that most descendant cells maintain silencing of that X chromosome. In eutherian mammals, XCI is thought to be triggered by the expression of the non-coding Xist RNA from the future inactive X chromosome (Xi); Xist RNA in turn is proposed to recruit protein complexes that bring about heterochromatinization of the Xi. Here we test whether imprinted XCI, which results in preferential inactivation of the paternal X chromosome (Xp), occurs in mouse embryos inheriting an Xp lacking Xist. We find that silencing of Xp-linked genes can initiate in the absence of paternal Xist; Xist is, however, required to stabilize silencing along the Xp. Xp-linked gene silencing associated with mouse imprinted XCI, therefore, can initiate in the embryo independently of Xist RNA.
Figures

References
-
- Brown CJ, et al. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;349:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Huynh KD, Lee JT. Inheritance of a pre-inactivated paternal X chromosome in early mouse embryos. Nature. 2003;426:857–862. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto I, Otte AP, Allis CD, Reinberg D, Heard E. Epigenetic dynamics of imprinted X inactivation during early mouse development. Science. 2004;303:644–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

