Population alterations of L-arginase- and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressed CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells and CD8+ T lymphocytes in patients with advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19572148
- PMCID: PMC11827779
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0634-0
Population alterations of L-arginase- and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressed CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells and CD8+ T lymphocytes in patients with advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Immune aberrations have been demonstrated in tumorogenesis, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) have shown to play a pivotal role in mediating immune suppression in animal models of human tumors. In the present study, we explored the clinical relevance of CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ MDSCs and the association of MDSCs with CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
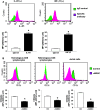
Patients and methods: The population of CD11b+/CD14⁻ cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNC) was determined in 173 patients with NSCLC and 42 control subjects. The expression of CD15, CD33, IL-4R, INF-γR, iNOS and L-arginase were analyzed. Cocultures with CD8+ T lymphocytes and Jurkat cells were developed to determine the impact of MDSCs on the expression of CD3ζ of CD8+ T lymphocytes.
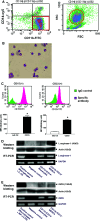
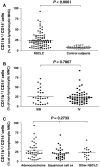
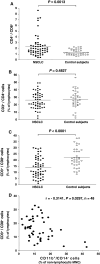
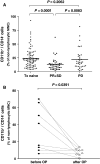
Results: Patients with treatment-naïve, advanced-stage NSCLC (n = 87) had an increased subpopulation of CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ cells in the PBMNCs with characteristics of MDSCs (P < 0.0001). The CD11b+/CD14⁻ cells in PBMNC also express IL-4R and INF-γR and can suppress CD3ζ expression in CD8+ T lymphocytes. The subpopulation of CD11b+/CD14⁻ cells in PBMNC was decreased in the advanced-stage NSCLC patients who had responsiveness to chemotherapy (n = 41, P < 0.0001) and in the early-stage NSCLC patients after removal of tumor (n = 8, P = 0.0391). Notably, a negative association existed between the population of CD11b+/CD14⁻ cells in PBMNC and the frequency of CD8+ T lymphocytes (n = 48, r = -0.3141, P = 0.0297).
Conclusions: Our study provided evidence of an increased pool of CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ MDSCs in the peripheral blood of NSCLC patients. For the suppressive effect of the cells on CD8+ T lymphocytes, these findings suggest the important role of the CD11b+/CD14⁻/CD15+/CD33+ MDSCs in mediating immunosuppression in NSCLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD14(+)S100A9(+) monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and their clinical relevance in non-small cell lung cancer.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Nov 15;186(10):1025-36. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201204-0636OC. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22955317 Free PMC article.
-
A circulating subpopulation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells as an independent prognostic/predictive factor in untreated non-small lung cancer patients.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:659294. doi: 10.1155/2014/659294. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25436215 Free PMC article.
-
CD45+CD33lowCD11bdim myeloid-derived suppressor cells suppress CD8+ T cell activity via the IL-6/IL-8-arginase I axis in human gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jul 9;9(7):763. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0803-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29988030 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy (excluding checkpoint inhibitors) for stage I to III non-small cell lung cancer treated with surgery or radiotherapy with curative intent.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 16;12(12):CD011300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011300.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 6;12:CD011300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011300.pub3. PMID: 29247502 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
Cited by
-
Natural Killer Cell Interactions With Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment and Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 5;12:633205. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.633205. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higher frequencies of GARP(+)CTLA-4(+)Foxp3(+) T regulatory cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients are associated with impaired T-cell functionality.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 15;73(8):2435-44. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3381. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23423978 Free PMC article.
-
Significant roles of regulatory T cells and myeloid derived suppressor cells in hepatitis B virus persistent infection and hepatitis B virus-related HCCs.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Feb 3;16(2):3307-22. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023307. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25654227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased CD14(+)HLA-DR (-/low) myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with extrathoracic metastasis and poor response to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Sep;62(9):1439-51. doi: 10.1007/s00262-013-1450-6. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23760662 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The complexity of neutrophils in health and disease: Focus on cancer.Semin Immunol. 2020 Apr;48:101409. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101409. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Semin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32958359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP, Gabrilovich DI (2001) Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients. A mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol 166:678–689 - PubMed
-
- Beasley MB, Brambilla E, Travis WD (2005) The 2004 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors. Semin Roentgenol 40:90–97 - PubMed
-
- Bosma GC, Custer RP, Bosma MJ (1983) A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature 301:527–530 - PubMed
-
- Bronte V, Serafini P, De Santo C, Marigo I, Tosello V, Mazzoni A, Segal DM, Staib C, Lowel M, Sutter G, Colombo MP, Zanovello P (2003) IL-4-induced arginase 1 suppresses alloreactive T cells in tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol 170:270–278 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

