Quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in healthy human brain using positron emission tomography and an inverse agonist radioligand
- PMID: 19573609
- PMCID: PMC2730982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.059
Quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in healthy human brain using positron emission tomography and an inverse agonist radioligand
Abstract
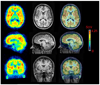
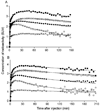
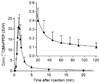
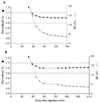
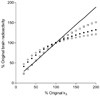
[11C]MePPEP is a high affinity, CB1 receptor-selective, inverse agonist that has been studied in rodents and monkeys. We examined the ability of [11C]MePPEP to quantify CB1 receptors in human brain as distribution volume calculated with the "gold standard" method of compartmental modeling and compared results with the simple measure of brain uptake. A total of 17 healthy subjects participated in 26 positron emission tomography (PET) scans, with 8 having two PET scans to assess retest variability. After injection of [11C]MePPEP, brain uptake of radioactivity was high (e.g., 3.6 SUV in putamen at approximately 60 min) and washed out very slowly. A two-tissue compartment model yielded values of distribution volume (which is proportional to receptor density) that were both well identified (SE 5%) and stable between 60 and 210 min. The simple measure of brain uptake (average concentration of radioactivity between 40 and 80 min) had good retest variability ( approximately 8%) and moderate intersubject variability (16%, coefficient of variation). In contrast, distribution volume had two-fold greater retest variability ( approximately 15%) and, thus, less precision. In addition, distribution volume had three-fold greater intersubject variability ( approximately 52%). The decreased precision of distribution volume compared to brain uptake was likely due to the slow washout of radioactivity from brain and to noise in measurements of the low concentrations of [11C]MePPEP in plasma. These results suggest that brain uptake can be used for within subject studies (e.g., to measure receptor occupancy by medications) but that distribution volume remains the gold standard for accurate measurements between groups.
Figures


References
-
- Abood ME, Ditto KE, Noel MA, Showalter VM, Tao Q. Isolation and expression of a mouse CB1 cannabinoid receptor gene. Comparison of binding properties with those of native CB1 receptors in mouse brain and N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997;53:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr AC. 1974;19:716–723.
-
- Bevington PR, Robinson DK. Data reduction and error analysis for the physical sciences. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003.
-
- Burger C, Mikolajczyk K, Grodzki M, Rudnicki P, Szabatin M, Buck A. JAVA tools quantitative post-processing of brain PET data. J Nucl Med. 1998;39 Suppl.:277P.
-
- Burns HD, Van Laere K, Sanabria-Bohorquez S, Hamill TG, Bormans G, Eng WS, Gibson R, Ryan C, Connolly B, Patel S, Krause S, Vanko A, Van Hecken A, Dupont P, De Lepeleire I, Rothenberg P, Stoch SA, Cote J, Hagmann WK, Jewell JP, Lin LS, Liu P, Goulet MT, Gottesdiener K, Wagner JA, de Hoon J, Mortelmans L, Fong TM, Hargreaves RJ. [18F]MK-9470, a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer for in vivo human PET brain imaging of the cannabinoid-1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 2007;104(23):9800–9805. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

