Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration
- PMID: 19573611
- PMCID: PMC2733527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.060
Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration
Abstract
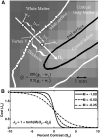
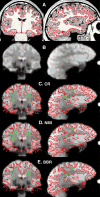
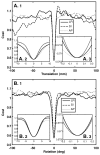
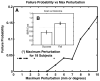
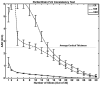
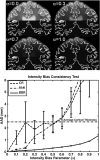
The fine spatial scales of the structures in the human brain represent an enormous challenge to the successful integration of information from different images for both within- and between-subject analysis. While many algorithms to register image pairs from the same subject exist, visual inspection shows that their accuracy and robustness to be suspect, particularly when there are strong intensity gradients and/or only part of the brain is imaged. This paper introduces a new algorithm called Boundary-Based Registration, or BBR. The novelty of BBR is that it treats the two images very differently. The reference image must be of sufficient resolution and quality to extract surfaces that separate tissue types. The input image is then aligned to the reference by maximizing the intensity gradient across tissue boundaries. Several lower quality images can be aligned through their alignment with the reference. Visual inspection and fMRI results show that BBR is more accurate than correlation ratio or normalized mutual information and is considerably more robust to even strong intensity inhomogeneities. BBR also excels at aligning partial-brain images to whole-brain images, a domain in which existing registration algorithms frequently fail. Even in the limit of registering a single slice, we show the BBR results to be robust and accurate.
Figures
References
-
- Borgefors G. Hierarchical chamfer matching: A parametric edge matching algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligience. 1988;10:849–865.
-
- Collins D, Dai W, Peters T, Evans A. Automatic 3d model-based neuroanatomical segmentation. Human Brain Mapping. 1995;3:190–208.
-
- Riviere D, Jr, Cointepas Y, Papadopoulos-Orfanos D, Cachia A, Mangin J-F. A freely available anatomist/brainvisa package for structural morphometry of the cortical sulci. Proceedings of Human Brain Mapping; 2003. p. 934.
-
- Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI. Cortical surface-based analysis i: Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage. 1999;9:179–194. - PubMed
-
- Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on mri scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage. 2006;31:968–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

