The human lipodystrophy gene product Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin plays a key role in adipocyte differentiation
- PMID: 19574402
- PMCID: PMC2754678
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-0236
The human lipodystrophy gene product Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin plays a key role in adipocyte differentiation
Abstract
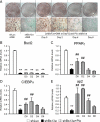
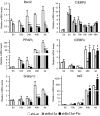
Mutations in the Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2 gene (BSCL2) are the underlying defect in patients with congenital generalized lipodystrophy type 2. BSCL2 encodes a protein called seipin, whose function is largely unknown. In this study, we investigated the role of Bscl2 in the regulation of adipocyte differentiation. Bscl2 mRNA is highly up-regulated during standard hormone-induced adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells in vitro. However, this up-regulation does not occur during mesenchymal stem cell (C3H10T1/2 cells) commitment to the preadipocyte lineage. Knockdown of Bscl2 by short hairpin RNA in C3H10T1/2 cells has no effect on bone morphogenetic protein-4-induced preadipocyte commitment. However, knockdown in 3T3-L1 cells prevents adipogenesis induced by a standard hormone cocktail, but adipogenesis can be rescued by the addition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist pioglitazone at an early stage of differentiation. Interestingly, pioglitazone-induced differentiation in the absence of standard hormone is not associated with up-regulated Bscl2 expression. On the other hand, short hairpin RNA-knockdown of Bscl2 largely blocks pioglitazone-induced adipose differentiation. These experiments suggest that Bscl2 may be essential for normal adipogenesis; it works upstream or at the level of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, enabling the latter to exert its full activity during adipogenesis. Loss of Bscl2 function thus interferes with the normal transcriptional cascade of adipogenesis during fat cell differentiation, resulting in near total loss of fat or lipodystrophy.
Figures




References
-
- Berardinelli W 1954 An undiagnosed endocrinometabolic syndrome: report of 2 cases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 14:193–204 - PubMed
-
- Seip M, Trygstad O 1996 Generalized lipodystrophy, congenital and acquired (lipoatrophy). Acta Paediatr Suppl 413:2–28 - PubMed
-
- Garg A, Wilson R, Barnes R, Arioglu E, Zaidi Z, Gurakan F, Kocak N, O'Rahilly S, Taylor SI, Patel SB, Bowcock AM 1999 A gene for congenital generalized lipodystrophy maps to human chromosome 9q34. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:3390–3394 - PubMed
-
- Magré J, Delépine M, Khallouf E, Gedde-Dahl Jr T, Van Maldergem L, Sobel E, Papp J, Meier M, Mégarbané A, Bachy A, Verloes A, d'Abronzo FH, Seemanova E, Assan R, Baudic N, Bourut C, Czernichow P, Huet F, Grigorescu F, de Kerdanet M, Lacombe D, Labrune P, Lanza M, Loret H, Matsuda F, et al. 2001 Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat Genet 28:365–370 - PubMed
-
- Kim CA, Delépine M, Boutet E, El Mourabit H, Le Lay S, Meier M, Nemani M, Bridel E, Leite CC, Bertola DR, Semple RK, O'Rahilly S, Dugail I, Capeau J, Lathrop M, Magré J 2008 Association of a homozygous nonsense caveolin-1 mutation with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1129–1134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

