Dioxin increases the interaction between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and estrogen receptor alpha at human promoters
- PMID: 19574409
- PMCID: PMC2999625
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp144
Dioxin increases the interaction between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and estrogen receptor alpha at human promoters
Abstract
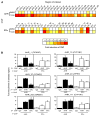
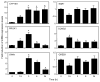
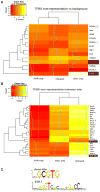
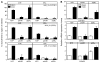
Recent studies have shown that activated aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) induced the recruitment of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) to AHR-regulated genes and that AHR is recruited to ERalpha-regulated genes. However, these findings were limited to a small number of well-characterized AHR- or ERalpha-responsive genes with little knowledge of what was occurring at other genomic regions. In this study, we showed using chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by hybridization to promoter focused microarrays (ChIP-chip) that 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin treatment significantly increased the overlap of genomic regions bound by both AHR and ERalpha. Conventional and sequential ChIPs confirmed the recruitment of AHR and ERalpha to many of the identified regions. Transcription factor binding site analysis revealed an overrepresentation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor response elements in regions bound by both AHR and ERalpha, suggesting that AHR was the important factor determining the recruitment of ERalpha to these regions. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of AHR confirmed its requirement for the recruitment of ERalpha to some, but not all, of the shared regions. Our findings demonstrate not only that dioxin induces the recruitment of ERalpha to AHR target genes but also that AHR is recruited to estrogen-responsive regions in a gene-specific manner, suggesting that AHR utilizes both of these mechanisms to modulate estrogen-dependent signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Angus WG, Larsen MC, Jefcoate CR. Expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 depends on cell-specific factors in human breast cancer cell lines: Role of estrogen receptor status. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:947–955. - PubMed
-
- Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Williams KJ, Zacharewski TR. Inhibition of estrogen-mediated uterine gene expression responses by dioxin. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:82–93. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS, Liu XS, Brodsky AS, Li W, Meyer CA, Szary AJ, Eeckhoute J, Shao W, Hestermann EV, Geistlinger TR, et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell. 2005;122:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS, Meyer CA, Song J, Li W, Geistlinger TR, Eeckhoute J, Brodsky AS, Keeton EK, Fertuck KC, Hall GF, et al. Genome-wide analysis of estrogen receptor binding sites. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1289–1297. - PubMed

