Diabetic albuminuria is due to a small fraction of nephrons distinguished by albumin-stained tubules and glomerular adhesions
- PMID: 19574429
- PMCID: PMC2716951
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080939
Diabetic albuminuria is due to a small fraction of nephrons distinguished by albumin-stained tubules and glomerular adhesions
Abstract
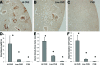
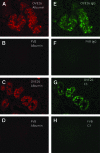
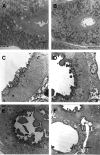
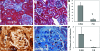
OVE26 diabetic mice develop severe albuminuria. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed a pattern of intense albumin staining in a small subset of OVE26 tubules. Immunostaining was strikingly heterogeneous; some tubules stained intensely for albumin, but most tubules had weak or no staining. Serial sectioning showed that staining patterns were distinctive for each nephron. Electron microscopy revealed that albumin accumulated in villi and at the base of the brush border. Tubule cell injury, as shown by loss of villi, tubule dilation, and cellular protrusions into the tubule lumen, was unambiguously associated with albumin staining. Examination of albumin staining of proteinuric human kidneys also showed a heterogeneous pattern of staining. Analysis of OVE26 serial sections indicated that all glomeruli connected to albumin-positive tubules were identified by albumin-stained lesions in the tuft that adhered to Bowman's capsule, implicating this as a critical feature of heavy albumin leakage. These results indicate that albumin accumulation provides a marker of damaged nephrons, and confirm that albumin leakage produces significant tubular damage. This study shows that that formation of sclerotic glomerular adhesions is a critical step leading to severe albuminuria.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Impaired Albumin Uptake and Processing Promote Albuminuria in OVE26 Diabetic Mice.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:8749417. doi: 10.1155/2016/8749417. Epub 2016 Oct 16. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27822483 Free PMC article.
-
The normal kidney filters nephrotic levels of albumin retrieved by proximal tubule cells: retrieval is disrupted in nephrotic states.Kidney Int. 2007 Mar;71(6):504-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002041. Epub 2007 Jan 17. Kidney Int. 2007. PMID: 17228368
-
Albumin stimulates renal tubular inflammation through an HSP70-TLR4 axis in mice with early diabetic nephropathy.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):1311-21. doi: 10.1242/dmm.019398. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26398934 Free PMC article.
-
Where does albuminuria come from in diabetic kidney disease?Curr Diab Rep. 2008 Dec;8(6):477-85. doi: 10.1007/s11892-008-0082-2. Curr Diab Rep. 2008. PMID: 18990305 Review.
-
Pathways to nephron loss starting from glomerular diseases-insights from animal models.Kidney Int. 2005 Feb;67(2):404-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.67097.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 15673288 Review.
Cited by
-
FVB mouse genotype confers susceptibility to OVE26 diabetic albuminuria.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):F487-94. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00018.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20610531 Free PMC article.
-
Mesangial Cell Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Activation Results in Mesangial Expansion.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Oct;28(10):2879-2885. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016111196. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28701517 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotection From Diabetic Complications in OVE Transgenic Mice by Endothelial Cell Specific Overexpression of Metallothionein: A TEM Stereological Analysis.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017 Mar;300(3):560-576. doi: 10.1002/ar.23511. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27813325 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous afferent arteriolopathy: a key concept for understanding blood pressure-dependent renal damage.Hypertens Res. 2024 Dec;47(12):3383-3396. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01916-z. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 39379463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Albumin-induced apoptosis of glomerular parietal epithelial cells is modulated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Apr;27(4):1330-43. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr483. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 21896500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molitoris BA, Sandoval RM. Intravital multiphoton microscopy of dynamic renal processes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288:F1084–F1089. - PubMed
-
- Qi Z, Fujita H, Jin J, Davis LS, Wang Y, Fogo AB, Breyer MD. Characterization of susceptibility of inbred mouse strains to diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2005;54:2628–2637. - PubMed
-
- Breyer MD. Stacking the deck for drug discovery in diabetic nephropathy: in search of an animal model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:1623–1624. - PubMed
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39:S1–266. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1676–1685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

