DNA binding by estrogen receptor-alpha is essential for the transcriptional response to estrogen in the liver and the uterus
- PMID: 19574448
- PMCID: PMC5419145
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0045
DNA binding by estrogen receptor-alpha is essential for the transcriptional response to estrogen in the liver and the uterus
Abstract
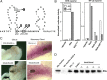
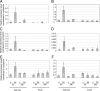
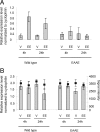
The majority of the biological effects of estrogens in the reproductive tract are mediated by estrogen receptor (ER)alpha, which regulates transcription by several mechanisms. Because the tissue-specific effects of some ERalpha ligands may be caused by tissue-specific transcriptional mechanisms of ERalpha, we aimed to identify the contribution of DNA recognition to these mechanisms in two clinically important target organs, namely uterus and liver. We used a genetic mouse model that dissects DNA binding-dependent vs. independent transcriptional regulation elicited by ERalpha. The EAAE mutant harbors amino acid exchanges at four positions of the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of ERalpha. This construct was knocked in the ERalpha gene locus to produce ERalpha((EAAE/EAAE)) mice devoid of a functional ERalpha DBD. The phenotype of the ERalpha((EAAE/EAAE)) mice resembles the general loss-of-function phenotype of alphaER knockout mutant mice with hypoplastic uteri, hemorrhagic ovaries, and impaired mammary gland development. In agreement with this phenotype, the expression pattern of the ERalpha((EAAE/EAAE)) mutant mice in liver obtained by genome-wide gene expression profiling supports the observation of a near-complete loss of estrogen-dependent gene regulation in comparison with the wild type. Further gene expression analyses to validate the results of the microarray data were performed by quantitative RT-PCR. The analyses indicate that both gene activation and repression by estrogen-bound ERalpha rely on an intact DBD in vivo.
Figures



References
-
- Hall JM, Couse JF, Korach KS2001. The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 276:36869–36872 - PubMed
-
- Shang Y, Brown M2002. Molecular determinants for the tissue specificity of SERMs. Science 295:2465–2468 - PubMed
-
- Castro-Rivera E, Samudio I, Safe S2001. Estrogen regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression in ZR-75 breast cancer cells involves multiple enhancer elements. J Biol Chem 276:30853–30861 - PubMed
-
- O'Brien JE, Peterson TJ, Tong MH, Lee EJ, Pfaff LE, Hewitt SC, Korach KS, Weiss J, Jameson JL2006. Estrogen-induced proliferation of uterine epithelial cells is independent of estrogen receptor α binding to classical estrogen response elements. J Biol Chem 281:26683–26692 - PubMed
-
- Dubik D, Shiu RP1992. Mechanism of estrogen activation of c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene 7:1587–1594 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

