Management of pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 19575243
- PMCID: PMC2899525
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-009-1073-y
Management of pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of the literature
Abstract
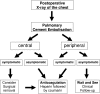
Balloon kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty are relatively recent procedures in the treatment of painful vertebral fractures. There are, however, still some uncertainties about the incidence and treatment strategies of pulmonary cement embolisms (PCE). In order to work out a treatment strategy for the management of this complication, we performed a review of the literature. The results show that there is no clear diagnostic or treatment standard for PCE. The literature research revealed that the risk of a pulmonary embolism ranges from 3.5 to 23% for osteoporotic fractures. In cases of asymptomatic patients with peripheral PCE we recommend no treatment besides clinical follow-up; in cases of symptomatic or central embolisms, however, we recommend to proceed according to the guidelines regarding the treatment of thrombotic pulmonary embolisms, which includes initial heparinization and a following 6-month coumarin therapy. In order to avoid any types of embolisms, both procedures should only be performed by experienced surgeons after critical determination of the indications.
Figures
References
-
- Anselmetti GC, Corgnier A, Debernardi F, Regge D. Treatment of painful compression vertebral fractures with vertebroplasty: results and complications. Radiol Med (Torino) 2005;110:262–272. - PubMed
-
- Anselmetti GC, Zoarski G, Manca A et al (2008) Percutaneous vertebroplasty and bone cement leakage: clinical experience with a new high-viscosity bone cement and delivery system for vertebral augmentation in benign and malignant compression fractures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical