Relation of multiple inflammatory biomarkers to incident atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 19576326
- PMCID: PMC2802058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.02.053
Relation of multiple inflammatory biomarkers to incident atrial fibrillation
Abstract
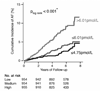
Basic and clinical studies have suggested that inflammation predisposes to atrial fibrillation (AF). We assessed the association of 12 circulating inflammatory biomarkers (i.e., C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, interleukin-6, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 [mass and activity], monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, myeloperoxidase, CD40 ligand, osteoprotegerin, P-selectin, and tumor necrosis factor receptor II) with incident AF in 2863 Framingham Offspring Study participants (mean age 60.7 years, SD = 9.4, 55% women). During follow-up (median 6 years), 148 participants (43% women) developed incident AF. In the multivariable proportional hazards models, the inflammatory biomarker panel was associated with incident AF (p = 0.03). With stepwise selection (p <0.01 for entry and retention), log-transformed osteoprotegerin was associated with incident AF (hazard ratio per SD 1.30, 95% confidence interval 1.08 to 1.56, p = 0.006). Adjusting for interim myocardial infarction or heart failure attenuated the association between osteoprotegerin and incident AF (hazard ratio 1.18, 95% confidence interval 0.98 to 1.43, p = 0.09). In conclusion, circulating osteoprotegerin concentration was significantly associated with incident AF in our community-based sample, possibly mediated by interim cardiovascular events.
Figures
References
-
- Nakamura Y, Nakamura K, Fukushima-Kusano K, Ohta K, Matsubara H, Hamuro T, Yutani C, Ohe T. Tissue factor expression in atrial endothelia associated with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: possible involvement in intracardiac thrombogenesis. Thromb Res. 2003;111:137–142. - PubMed
-
- Roldan V, Marin F, Blann AD, Garcia A, Marco P, Sogorb F, Lip GY. Interleukin-6, endothelial activation and thrombogenesis in chronic atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1373–1380. - PubMed
-
- Chung MK, Martin DO, Sprecher D, Wazni O, Kanderian A, Carnes CA, Bauer JA, Tchou PJ, Niebauer MJ, Natale A, Van Wagoner DR. C-reactive protein elevation in patients with atrial arrhythmias: inflammatory mechanisms and persistence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2001;104:2886–2891. - PubMed
-
- Aviles RJ, Martin DO, pperson-Hansen C, Houghtaling PL, Rautaharju P, Kronmal RA, Tracy RP, Van Wagoner DR, Psaty BM, Lauer MS, Chung MK. Inflammation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;108:3006–3010. - PubMed
-
- Mukamal KJ, Tolstrup JS, Friberg J, Gronbaek M, Jensen G. Fibrinogen and albumin levels and risk of atrial fibrillation in men and women (the Copenhagen City Heart Study) Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:75–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064753/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL004334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1 K23 HL083102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01 HL71039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL083102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL04334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL064753/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 6R01-NS 17950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials