An immunohistochemical procedure to detect patients with paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma with germline SDHB, SDHC, or SDHD gene mutations: a retrospective and prospective analysis
- PMID: 19576851
- PMCID: PMC4718191
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70164-0
An immunohistochemical procedure to detect patients with paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma with germline SDHB, SDHC, or SDHD gene mutations: a retrospective and prospective analysis
Abstract
Background: Phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas are neuro-endocrine tumours that occur sporadically and in several hereditary tumour syndromes, including the phaeochromocytoma-paraganglioma syndrome. This syndrome is caused by germline mutations in succinate dehydrogenase B (SDHB), C (SDHC), or D (SDHD) genes. Clinically, the phaeochromocytoma-paraganglioma syndrome is often unrecognised, although 10-30% of apparently sporadic phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas harbour germline SDH-gene mutations. Despite these figures, the screening of phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas for mutations in the SDH genes to detect phaeochromocytoma-paraganglioma syndrome is rarely done because of time and financial constraints. We investigated whether SDHB immunohistochemistry could effectively discriminate between SDH-related and non-SDH-related phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas in large retrospective and prospective tumour series.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry for SDHB was done on 220 tumours. Two retrospective series of 175 phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas with known germline mutation status for phaeochromocytoma-susceptibility or paraganglioma-susceptibility genes were investigated. Additionally, a prospective series of 45 phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas was investigated for SDHB immunostaining followed by SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD mutation testing.
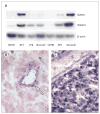
Findings: SDHB protein expression was absent in all 102 phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas with an SDHB, SDHC, or SDHD mutation, but was present in all 65 paraganglionic tumours related to multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, von Hippel-Lindau disease, and neurofibromatosis type 1. 47 (89%) of the 53 phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas with no syndromic germline mutation showed SDHB expression. The sensitivity and specificity of the SDHB immunohistochemistry to detect the presence of an SDH mutation in the prospective series were 100% (95% CI 87-100) and 84% (60-97), respectively.
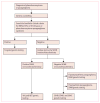
Interpretation: Phaeochromocytoma-paraganglioma syndrome can be diagnosed reliably by an immunohistochemical procedure. SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD germline mutation testing is indicated only in patients with SDHB-negative tumours. SDHB immunohistochemistry on phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas could improve the diagnosis of phaeochromocytoma-paraganglioma syndrome.
Funding: The Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, Dutch Cancer Society, Vanderes Foundation, Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, and a PHRC grant COMETE 3 for the COMETE network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diagnosing patients with hereditary paraganglial tumours.Lancet Oncol. 2009 Aug;10(8):741. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70204-9. Lancet Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19647193 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M, Pacak K. Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet. 2005;366:665–75. - PubMed
-
- Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP, Athyros VG, Harsoulis F. Phaeochromocytoma: an update on genetics and management. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14:935–56. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura E, Kaelin WG., Jr Recent insights into the molecular pathogenesis of phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Endocr Pathol. 2006;17:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Amar L, Bertherat J, Baudin E, et al. Genetic testing in phaeochromocytoma or functional paraganglioma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8812–18. - PubMed
-
- Lancaster CR. Succinate:quinone oxidoreductases: an overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1553:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

