PDGF-mediated protection of SH-SY5Y cells against Tat toxin involves regulation of extracellular glutamate and intracellular calcium
- PMID: 19576918
- PMCID: PMC2753679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.06.020
PDGF-mediated protection of SH-SY5Y cells against Tat toxin involves regulation of extracellular glutamate and intracellular calcium
Abstract
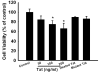
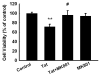
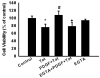
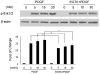
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protein Tat has been implicated in mediating neuronal apoptosis, one of the hallmark features of HIV-associated dementia (HAD). Mitigation of the toxic effects of Tat could thus be a potential mechanism for reducing HIV toxicity in the brain. In this study we demonstrated that Tat-induced neurotoxicity was abolished by NMDA antagonist-MK801, suggesting the role of glutamate in this process. Furthermore, we also found that pretreatment of SH-SY5Y cells with PDGF exerted protection against Tat toxicity by decreasing extracellular glutamate levels. We also demonstrated that extracellular calcium chelator EGTA was able to abolish PDGF-mediated neuroprotection, thereby underscoring the role of calcium signaling in PDGF-mediated neuroprotection. We also showed that Erk signaling pathway was critical for PDGF-mediated protection of cells. Additionally, blocking calcium entry with EGTA resulted in suppression of PDGF-induced Erk activation. These findings thus underscore the role of PDGF-mediated calcium signaling and Erk phosphorylation in the protection of cells against HIV Tat toxicity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TRPC channel-mediated neuroprotection by PDGF involves Pyk2/ERK/CREB pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2009 Dec;16(12):1681-93. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.108. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 19680266 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-derived growth factor protects neurons against gp120-mediated toxicity.J Neurovirol. 2008 Jan;14(1):62-72. doi: 10.1080/13550280701809084. J Neurovirol. 2008. PMID: 18300076 Free PMC article.
-
MCP-1 (CCL2) protects human neurons and astrocytes from NMDA or HIV-tat-induced apoptosis.J Neurochem. 2003 Jun;85(5):1299-311. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01775.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12753088
-
Platelet-derived growth factor CC-mediated neuroprotection against HIV Tat involves TRPC-mediated inactivation of GSK 3beta.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047572. Epub 2012 Oct 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23077641 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB in Restoring HIV Tat-Cocaine-Mediated Impairment of Neuronal Differentiation.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6377-6387. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9536-0. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26572642 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of morphine-induced synaptic alterations: Role of oxidative stress, ER stress, and autophagy.J Cell Biol. 2016 Oct 24;215(2):245-258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201605065. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27810915 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone protects normative anxiety-like responding among ovariectomized female mice that conditionally express the HIV-1 regulatory protein, Tat, in the CNS.Horm Behav. 2014 May;65(5):445-53. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Horm Behav. 2014. PMID: 24726788 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of intranasal extracellular vesicles from human platelet concentrates supernatants in traumatic brain injury and Parkinson's disease models.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Sep 5;31(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01072-z. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 39237980 Free PMC article.
-
Oligodendrocytes Are Targets of HIV-1 Tat: NMDA and AMPA Receptor-Mediated Effects on Survival and Development.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 12;35(32):11384-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4740-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26269645 Free PMC article.
-
A growth factor attenuates HIV-1 Tat and morphine induced damage to human neurons: implication in HIV/AIDS-drug abuse cases.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 24;6(3):e18116. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018116. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albright AV, Soldan SS, Gonzalez-Scarano F. Pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus-induced neurological disease. J Neurovirol. 2003;9:222–227. - PubMed
-
- Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1329–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bachis A, Mocchetti I. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is neuroprotective against human immunodeficiency virus-1 envelope proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1053:247–257. - PubMed
-
- Bell JE. The neuropathology of adult HIV infection. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1998;154:816–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

