PDGF-mediated protection of SH-SY5Y cells against Tat toxin involves regulation of extracellular glutamate and intracellular calcium
- PMID: 19576918
- PMCID: PMC2753679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.06.020
PDGF-mediated protection of SH-SY5Y cells against Tat toxin involves regulation of extracellular glutamate and intracellular calcium
Abstract
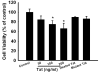
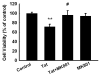
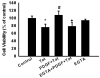
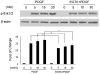
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protein Tat has been implicated in mediating neuronal apoptosis, one of the hallmark features of HIV-associated dementia (HAD). Mitigation of the toxic effects of Tat could thus be a potential mechanism for reducing HIV toxicity in the brain. In this study we demonstrated that Tat-induced neurotoxicity was abolished by NMDA antagonist-MK801, suggesting the role of glutamate in this process. Furthermore, we also found that pretreatment of SH-SY5Y cells with PDGF exerted protection against Tat toxicity by decreasing extracellular glutamate levels. We also demonstrated that extracellular calcium chelator EGTA was able to abolish PDGF-mediated neuroprotection, thereby underscoring the role of calcium signaling in PDGF-mediated neuroprotection. We also showed that Erk signaling pathway was critical for PDGF-mediated protection of cells. Additionally, blocking calcium entry with EGTA resulted in suppression of PDGF-induced Erk activation. These findings thus underscore the role of PDGF-mediated calcium signaling and Erk phosphorylation in the protection of cells against HIV Tat toxicity.
Figures



References
-
- Albright AV, Soldan SS, Gonzalez-Scarano F. Pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus-induced neurological disease. J Neurovirol. 2003;9:222–227. - PubMed
-
- Almeida RD, Manadas BJ, Melo CV, Gomes JR, Mendes CS, Graos MM, Carvalho RF, Carvalho AP, Duarte CB. Neuroprotection by BDNF against glutamate-induced apoptotic cell death is mediated by ERK and PI3-kinase pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:1329–1343. - PubMed
-
- Bachis A, Mocchetti I. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is neuroprotective against human immunodeficiency virus-1 envelope proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1053:247–257. - PubMed
-
- Bell JE. The neuropathology of adult HIV infection. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1998;154:816–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

