Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota
- PMID: 19577011
- PMCID: PMC3026355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.06.023
Epidemiology of eosinophilic esophagitis over three decades in Olmsted County, Minnesota
Abstract
Background & aims: Data on secular trends and outcomes of eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) are scarce. We performed a population-based study to assess the epidemiology and outcomes of EE in Olmsted County, Minnesota, over the last 3 decades.
Methods: All cases of EE diagnosed between 1976 and 2005 were identified using the Rochester Epidemiology Project resources. Esophageal biopsies with any evidence of esophagitis and/or eosinophilic infiltration were reviewed by a single pathologist. Clinical course (treatment, response, and recurrence) was defined using information collected from medical records and prospectively via a telephone questionnaire. Incidence rates per 100,000 person years were directly adjusted for age and sex to the US 2000 population structure.
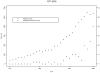
Results: A total of 78 patients with EE were identified. The incidence of EE increased significantly over the last 3 of the 5-year intervals (from 0.35 [95% confidence interval (CI)], 0-0.87] per 100,000 person-years during 1991-1995 to 9.45 [95% CI, 7.13-11.77] per 100,000 person-years during 2001-2005). The prevalence of EE was 55.0 (95% CI, 42.7-67.2) per 100,000 persons as of January 1, 2006, in Olmsted County, Minnesota. EE was diagnosed more frequently in late summer/fall. The clinical course of patients with EE was characterized by recurrent symptoms (observed in 41% of patients).
Conclusions: The prevalence and incidence of EE is higher than previously reported. The incidence of clinically diagnosed EE increased significantly over the last 3 decades, in parallel with endoscopy volume. Seasonal incidence was greatest in late summer and fall. EE also appears to be a recurrent relapsing disease in a substantial proportion of patients.
Figures



References
-
- Picus D, Frank PH. Eosinophilic esophagitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981;136:1001–3. - PubMed
-
- Potter JW, Saeian K, Staff D, Massey BT, Komorowski RA, Shaker R, Hogan WJ. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: an emerging problem with unique esophageal features. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:355–61. - PubMed
-
- Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:940–1. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003;37 (Suppl 1):S23–8. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, Verma R, Mascarenhas M, Semeao E, Flick J, Kelly J, Brown-Whitehorn T, Mamula P, Markowitz JE. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A 10-Year Experience in 381 Children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:1198–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

