Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-stimulated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha mediates estrogen receptor-alpha-induced mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth factor production
- PMID: 19577074
- PMCID: PMC2929584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.03.010
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-stimulated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha mediates estrogen receptor-alpha-induced mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth factor production
Abstract
Objective: Vascular endothelial growth factor, a critical factor in angiogenesis, mediates stem cell paracrine protective effects on ischemic myocardium. Studies on the role of sex in stem cell function have demonstrated that female mesenchymal stem cells produce greater vascular endothelial growth factor and provide better cardiac protection compared with male mesenchymal stem cells. The purpose of this study was to determine the mechanisms by which estrogen affects mesenchymal stem cell function as a potential therapeutic measure during ex vivo expansion, before therapeutic use.
Methods: A single-step purification method using adhesion to cell culture plastic was adopted to isolate mesenchymal stem cells from wild-type, estrogen receptor-alpha knockout, estrogen receptor-beta knockout, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 knockout mice. Mesenchymal stem cells were treated with or without 17beta-estradiol, estrogen receptor-alpha agonist (propyl pyrazoletriol), and estrogen receptor-beta agonist (diarylpropionitrile).
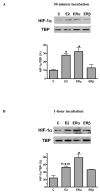
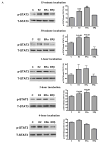
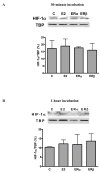
Results: 17beta-estradiol significantly increased mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth factor production in a dose-dependent manner. Both estrogen receptor-alpha and estrogen receptor-beta were expressed in mesenchymal stem cells. Administration of 17beta-estradiol or estrogen receptor-alpha agonist (not estrogen receptor-beta agonist) elevated mesenchymal stem cell vascular endothelial growth factor, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation. However, these effects were neutralized in estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mesenchymal stem cells, not estrogen receptor-beta knockout. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 knockout abolished estrogen receptor-alpha-induced hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and subsequent vascular endothelial growth factor production.
Conclusion: 17beta-estradiol-induced vascular endothelial growth factor production from mesenchymal stem cells appears to be mediated through estrogen receptor-alpha-activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha expression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hypoxia Upregulates Estrogen Receptor β in Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells in a HIF-1α-Dependent Manner.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Jul;59(1):114-126. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0167OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29394091 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen modulates in vitro T cell responses in a concentration- and receptor-dependent manner: effects on intracellular molecular targets and antioxidant enzymes.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):328-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.226. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911387
-
Estradiol's salutary effects on keratinocytes following trauma-hemorrhage are mediated by estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha and ER-beta.Mol Med. 2008 Nov-Dec;14(11-12):689-96. doi: 10.2119/2008-00068.Moeinpour. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18769638 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of estrogen receptor subtypes, ERα, ERβ, and GPER1 in rapid estradiol-mediated enhancement of hippocampal synaptic transmission in mice.Hippocampus. 2015 Dec;25(12):1556-66. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22475. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Hippocampus. 2015. PMID: 25980457 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue compartment-specific role of estrogen receptor subtypes in immune cell cytokine production following trauma-hemorrhage.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Jan;102(1):163-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00964.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 5. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007. PMID: 17023568
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Interferon-Gamma and Hypoxia-Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles: Underlying Mechanisms and Potentials in Clinical Translation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 20;12(6):1369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061369. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapy via oral administration of attenuated Salmonella expression plasmid-vectored Stat3-shRNA cures orthotopically transplanted mouse HCC.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Jun;19(6):393-401. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.12. Epub 2012 May 4. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22555509 Free PMC article.
-
Gender dimorphisms in progenitor and stem cell function in cardiovascular disease.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010 Apr;3(2):103-13. doi: 10.1007/s12265-009-9149-y. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2010. PMID: 20376198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR4 inhibits mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) STAT3 activation and thereby exerts deleterious effects on MSC-mediated cardioprotection.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 3;5(12):e14206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014206. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21151968 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin signaling is required for augmented therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells conferred by hypoxia preconditioning.Stem Cells. 2014 Oct;32(10):2702-13. doi: 10.1002/stem.1784. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24989835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crisostomo PR, Meldrum DR. Stem cell delivery to the heart: Clarifying methodology and mechanism. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2654–6. - PubMed
-
- Markel TA, Wang Y, Herrmann JL, Crisostomo PR, Wang M, Novotny NM, et al. VEGF is critical for stem cell-mediated cardioprotection and a crucial paracrine factor for defining the age threshold in adult and neonatal stem cell function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;295:H2308–14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uemura R, Xu M, Ahmad N, Ashraf M. Bone marrow stem cells prevent left ventricular remodeling of ischemic heart through paracrine signaling. Circ Res. 2006;98:1414–21. - PubMed
-
- Lin H, Shabbir A, Molnar M, Yang J, Marion S, Canty JM, Jr, et al. Adenoviral expression of vascular endothelial growth factor splice variants differentially regulate bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2008;216:458–68. - PubMed
-
- Payne TR, Oshima H, Okada M, Momoi N, Tobita K, Keller BB, et al. A relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor, angiogenesis, and cardiac repair after muscle stem cell transplantation into ischemic hearts. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1677–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

