Safety and immunogenicity of a subvirion inactivated influenza A/H5N1 vaccine with or without aluminum hydroxide among healthy elderly adults
- PMID: 19577636
- PMCID: PMC2730950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.06.057
Safety and immunogenicity of a subvirion inactivated influenza A/H5N1 vaccine with or without aluminum hydroxide among healthy elderly adults
Abstract
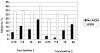
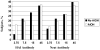
A total of 600 healthy adults > or =65 years were randomized to receive 2 vaccinations 1 month apart of a subvirion avian influenza A/H5N1 vaccine containing 3.75, 7.5, 15, or 45microg of hemagglutinin (HA) with or without aluminum hydroxide (AlOH). All formulations were safe. Groups given the vaccine with AlOH had more injection site discomfort. Dose-related increases in antibody responses were noted after the second vaccination. Antibody responses to the vaccine were not enhanced by AlOH at any HA dose level. A microneutralization titer > or =40 was observed in 36% and 40% of subjects who received 45microg of HA with or without AlOH, respectively.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00294099.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO strategic action plan for pandemic influenza. [April 25, 2009]. Available at: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/influenza/StregPlanEPR_GIP....
-
- Treanor JJ, Campbell JD, Zangwill KM, Rowe T, Wolff M. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated subvirion influenza A (H5N1) vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(13):1343–51. - PubMed
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first U.S. vaccine for humans against the avian influenza virus H5N1. [April 25, 2009]. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/NEWS/2007/NEW01611.html.
-
- Beyer WE, Palache AM, Baljet M, Masurel N. Antibody induction by influenza vaccines in the elderly: a review of the literature. Vaccine. 1989;7(5):385–94. - PubMed
-
- Hehme N, Engelmann H, Künzel W, Neumeier E, Sänger R. Pandemic preparedness: lessons learnt from H2N2 and H9N2 candidate vaccines. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2002;191(34):203–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K12 RR023250/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-25461/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025461/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025460/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI045250/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-25465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12RR023250/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-30068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-45250/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025459/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

