Treatment of depressive disorders
- PMID: 19578410
- PMCID: PMC2697009
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2008.0782
Treatment of depressive disorders
Abstract
Introduction: A confusing variety of options are available for the treatment of depressive disorders.
Method: Selective literature review under consideration of current guidelines.
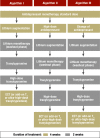
Results: The treatment of depression can be divided into acute, maintenance and prophylactic phases. The basic forms of treatment are pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and supportive strategies. The approximately 30 antidepressants currently on the market differ mainly with respect to their side effect profiles. Of the specific types of psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, psychodynamic therapy, and psychoanalysis are funded by the statutory health insurance providers in Germany. All treatment strategies (except for sleep deprivation) show a latency of onset of several weeks and a nonresponse rate of about 30% to 50%. In clinical practice it is essential to follow a stepwise procedure and to perform a standardized evaluation of response after the latency period. In the event of nonresponse, the next step of treatment should be initiated.
Discussion: Depressive disorders have a good prognosis provided one takes best advantage of the available treatment options. Preconditions are continuation of treatment for an appropriate length of time (for antidepressants ca. 4 to 6 weeks, for psychotherapy ca. 4 to 12 weeks) and standardized evaluation of response thereafter.
Keywords: antidepressants; depression; psychotherapy; stepwise antidepressant treatment; treatment algorithm.
Figures
Similar articles
-
REVAMP - Research Evaluating the Value of Augmenting Medication with Psychotherapy: rationale and design.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2008;41(4):5-33. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2008. PMID: 19015627 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
-
Relapse prevention in recurrent major depressive disorder. A comparison of different treatment options based on clinical experience and a critical review of the literature.Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2020 Nov;24(4):341-348. doi: 10.1080/13651501.2020.1779308. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32716222 Review.
-
Systematic reviews of randomised clinical trials examining the effects of psychotherapeutic interventions versus "no intervention" for acute major depressive disorder and a randomised trial examining the effects of "third wave" cognitive therapy versus mentalization-based treatment for acute major depressive disorder.Dan Med J. 2014 Oct;61(10):B4942. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25283628
-
Identifying patients at risk of complete nonresponse in the outpatient treatment of depression.Psychother Psychosom. 2008;77(6):358-64. doi: 10.1159/000151389. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Psychother Psychosom. 2008. PMID: 18701832
Cited by
-
Misleading statements.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009 May;106(18):319-20; author reply 321-2. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2009.0320a. Epub 2009 May 1. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009. PMID: 19547652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pirlindole in the treatment of depression: a meta-analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(1):61-71. doi: 10.2165/11586690-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21053988
-
Chronic and treatment resistant depression: diagnosis and stepwise therapy.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014 Nov 7;111(45):766-75; quiz 775. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2014.0766. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014. PMID: 25467053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Assessment of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Clinical Routine: A 3-Year Analysis of Life-Threatening Events in More Than 3,000 Treatment Sessions.Front Psychol. 2021 Nov 23;12:767915. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.767915. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34887815 Free PMC article.
-
SANRA-a scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles.Res Integr Peer Rev. 2019 Mar 26;4:5. doi: 10.1186/s41073-019-0064-8. eCollection 2019. Res Integr Peer Rev. 2019. PMID: 30962953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudolf S, Bermejo I, Schweiger U, Hohagen F, Härter M. Zertifizierte medizinische Fortbildung: Diagnostik depressiver Störungen. Dtsch Arztebl. 2006;103(25):A 1754–A 1762.
-
- Pöldinger W. Kompendium der Psychopharmakotherapie. Grenzach/Baden: Hoffmann-La Roche AG. 1971
-
- Kupfer DJ. Management of recurrent depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993;54(suppl. 2):29–33. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M, Bschor T, Pfennig A, Whybrow PC, Angst J, Versiani M, Möller HJ. WFSBP Task Force on Unipolar Depressive Disorders: World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Unipolar Depressive Disorders in Primary Care. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2007;8:67–104. - PubMed
-
- AkdÄ - Arzneimittelkommission der deutschen Ärzteschaft. Empfehlungen zur Therapie der Depression. 2. Auflage. Arzneiverordnung in der Praxis (Therapieempfehlungen) 2006 Juli;Band 33 Sonderheft 1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

